Consult your healthcare provider to determine if Clomiphene is the right choice for you. This medication primarily stimulates ovulation and is often prescribed for women experiencing infertility due to anovulation. By blocking estrogen receptors, Clomiphene encourages the pituitary gland to increase the production of hormones that support ovulation.
Before starting Clomiphene, discuss your medical history with your doctor, especially any existing health conditions such as liver disease or ovarian cysts. Regular monitoring during treatment is essential, as it helps track your response and adjust dosages as necessary. Typically, Clomiphene is taken for five days at the beginning of your menstrual cycle, with follow-up visits scheduled to monitor progress.
Be aware of potential side effects, which may include mood swings, hot flashes, or headaches. Some women report experiencing multiple pregnancies, so it’s important to have a candid discussion about risks and benefits with your provider. With the right approach and guidance, Clomiphene can be a valuable option in your fertility journey.
- Clomiphene Prescription: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Clomiphene: Uses and Indications
- Primary Uses of Clomiphene
- Indications for Clomiphene Prescription
- Who Should Consider a Clomiphene Prescription?
- Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Men with Low Sperm Count
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration of Clomiphene
- Administration Instructions
- Monitoring and Adjustments
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Clomiphene
- Less Common But Serious Risks
- Long-Term Considerations
- Monitoring and Follow-Up During Clomiphene Treatment
Clomiphene Prescription: A Comprehensive Guide
For individuals struggling with infertility, a healthcare provider may prescribe clomiphene citrate, commonly known as Clomid. This medication stimulates ovulation by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, prompting the pituitary gland to release hormones that encourage follicle growth.
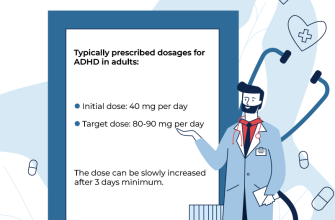
The typical starting dose is 50 mg per day for five days, usually taken within the first week of the menstrual cycle. Physicians may adjust the dosage based on the patient’s response; some may require an increase to 100 mg per day in subsequent cycles. Monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds helps track ovarian response and adjust doses as necessary.
Consider potential side effects such as hot flashes, mood swings, and altered cervical mucus. These symptoms may resolve after treatment ends. Important risks include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) and multiple pregnancies, which require careful patient evaluation and counseling. Always report any severe abdominal pain, dizziness, or nausea to a healthcare provider.
Patients should persistently document their menstrual cycles and symptoms. This information assists healthcare providers in tailoring the treatment plan effectively. For those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), clomiphene is often a first-line treatment due to its effectiveness in inducing ovulation.
Before starting clomiphene, discuss medical history with a healthcare provider. Certain conditions, such as liver disease or undiagnosed vaginal bleeding, may contraindicate its use. Regular follow-ups allow monitoring of side effects and overall treatment effectiveness.
Overall, clomiphene can be a valuable tool for those seeking to conceive. Adhering to prescribed guidelines and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals enhances treatment outcomes.
Understanding Clomiphene: Uses and Indications
Clomiphene is primarily prescribed to stimulate ovulation in women experiencing infertility. It is particularly effective for those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or irregular menstrual cycles. The medication works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, leading the body to increase the production of hormones responsible for ovulation.
Primary Uses of Clomiphene
Clomiphene is utilized in various situations including:
| Use | Description |
|---|---|
| Ovulation Induction | Stimulates the ovaries to produce eggs. |
| Infertility Treatment | Addresses specific forms of infertility related to ovulation issues. |
| Assessing Pituitary Function | Helps to evaluate the functioning of the pituitary gland. |
Indications for Clomiphene Prescription
This medication is typically recommended for:
- Women with diagnosed anovulation or oligoovulation.
- Certain cases of unexplained infertility.
- Women looking to conceive after prior infertility treatments have failed.
Monitoring during treatment is crucial. Healthcare providers usually schedule ultrasounds to assess follicle development and blood tests to measure hormone levels. Adjustments to dosage may be necessary based on individual responses to the medication. Regular follow-ups ensure safety and effectiveness in the treatment process.
Who Should Consider a Clomiphene Prescription?
Those facing difficulties in conceiving after trying for at least 12 months should discuss the potential of Clomiphene with their healthcare provider. Clomiphene is particularly beneficial for women with ovulatory disorders, which may hinder regular ovulation cycles. A medical evaluation can help confirm whether this medication is suitable.
Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Women diagnosed with PCOS often experience irregular periods and may not ovulate regularly. Clomiphene can stimulate ovulation, enhancing the chances of conception. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider ensures proper dosage and minimizes risks.
Men with Low Sperm Count
Men experiencing low sperm production may also benefit from Clomiphene. A healthcare provider might recommend this medication to improve hormone levels, potentially increasing sperm count. A thorough evaluation and consultation are essential to determine if Clomiphene is the right choice.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration of Clomiphene
The typical starting dose of clomiphene citrate is 50 mg, taken once daily for five days, beginning on the third to fifth day of the menstrual cycle. Monitoring for ovulation can begin 7 to 10 days after completing the course. If ovulation does not occur, the dose may be increased in subsequent cycles, usually up to a maximum of 150 mg per day.
Administration Instructions
Take clomiphene at the same time each day for consistency. Swallow the tablet whole with a full glass of water; do not chew or crush it. Ensure adequate hydration and a balanced diet throughout the treatment period to support overall health.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Clomiphene can lead to several side effects that users should monitor closely. Common experiences include hot flashes, mood swings, and breast tenderness. These symptoms often arise during treatment and generally subside after discontinuation.
Less Common But Serious Risks
Some individuals may experience visual disturbances, such as blurred vision or seeing spots. These effects, though rare, warrant immediate attention from a healthcare provider. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is another risk, characterized by swollen ovaries and abdominal discomfort. If symptoms escalate, such as severe abdominal pain or shortness of breath, seeking prompt medical help is crucial.
Long-Term Considerations
Long-term use of Clomiphene may increase the risk of certain cancers, particularly ovarian cancer. Regular screenings and consultations with a healthcare professional help in managing these risks effectively. Staying informed about your health and any changes experienced during treatment is an important strategy for those considering Clomiphene for fertility issues.
Monitoring and Follow-Up During Clomiphene Treatment
Regular monitoring is key to successful Clomiphene therapy. Schedule follow-up appointments to assess progress and adjust dosages if needed.
- Initial Assessment: Perform a thorough evaluation before starting treatment, including hormonal blood tests and an ultrasound to ensure no underlying conditions interfere.
- Cycle Tracking: Monitor menstrual cycles to determine the ovulation response. Keep a log of cycle length and any changes in symptoms.
- Hormonal Testing: Conduct serum progesterone tests about a week after expected ovulation. This helps confirm ovulation has occurred.
- Ultrasound Monitoring: Use transvaginal ultrasound to track follicular development and ovulation. This is particularly useful for assessing multiple follicle maturation.
- Side Effects Review: Discuss any side effects experienced, such as mood swings, hot flashes, or visual disturbances, during follow-up visits.
- Follow-Up Blood Work: Consider additional blood tests if ovulation hasn’t occurred after three cycles of treatment. This may help identify other hormonal imbalances.
After three to six cycles, review the entire treatment outcome and determine next steps. If pregnancy has not occurred, explore alternative fertility options or additional treatments.
Ensure clear communication about the goals of treatment and any concerns that arise during the process. Building a strong partnership with the prescriber enhances the overall experience and outcomes.