For individuals seeking an affordable solution for hair loss or prostate enlargement, the generic form of finasteride stands out as a reliable option. This medication operates by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to these conditions. Users can experience hair regrowth or a reduction in prostate size without the premium price tag of brand-name alternatives.
Choosing the generic version offers the same active ingredient, dosage, and efficacy as its branded counterpart. Patients often report similar outcomes when using generic finasteride, making it a smart choice for both budget-conscious consumers and those prioritizing treatment effectiveness.
Consulting with a healthcare provider remains crucial before starting any medication. They can provide tailored advice on usage and potential side effects. In this way, users can ensure they navigate their health decisions with confidence, maximizing the benefits of finasteride while minimizing risks.
- Drug Generic Form of Finasteride
- Overview of Finasteride: Mechanism and Uses
- Differences Between Brand Name and Generic Finasteride
- Cost
- Ingredients and Formulation
- Dosage Forms and Recommendations for Generic Finasteride
- Safety, Side Effects, and Contraindications of Finasteride
- Cost Comparison: Generic versus Brand Name Finasteride
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Generic Finasteride
Drug Generic Form of Finasteride
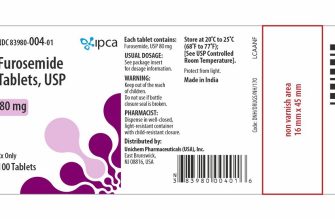
The generic form of Finasteride is available and commonly used for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness. This medication effectively blocks the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), leading to reduced prostate size and hair regrowth.
When considering generic Finasteride, you will find it available in several strengths, typically 1 mg and 5 mg tablets. Selecting the appropriate dosage depends on your specific condition:
- 1 mg: Primarily used for male pattern hair loss.
- 5 mg: Used for treating BPH and managing urinary symptoms.
Consult your healthcare provider to determine the right dosage for you. Adhering to the prescribed schedule enhances treatment success.
Generic Finasteride offers several benefits:
- Cost-effective compared to brand-name options.
- Same active ingredient and therapeutic effects as branded alternatives.
- Widely available at pharmacies and online.
Side effects may include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and breast tenderness. Keep an open line of communication with your doctor regarding any symptoms you experience. They can provide support and, if necessary, adjust your medication.
Potential interactions with other medications may occur. Inform your doctor about all prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements you take to avoid complications.
For best results, take the tablet consistently at the same time each day. Do not crush or chew the tablet; swallow it whole with water. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are recommended to monitor your progress and make adjustments if needed.
In summary, generic Finasteride serves as an effective option for managing both hair loss and prostate issues. Discuss your treatment plan with your doctor for personalized guidance.
Overview of Finasteride: Mechanism and Uses
Finasteride blocks the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. This reduction in DHT levels is beneficial for several conditions related to hair loss and prostate health.
Primarily, finasteride treats male pattern baldness by slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth. As DHT causes hair follicle shrinkage, lowering its levels can help maintain hair density, particularly in the crown and vertex of the scalp. For optimal results, it is advised to use finasteride consistently for at least three months, as visible benefits may take time to appear.
In addition, finasteride is effective in managing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). By decreasing prostate size, it alleviates urinary symptoms, such as frequent urination and difficulty in starting urination. For BPH patients, the recommended dosage is typically 5 mg daily, which can lead to significant improvements in quality of life over a period of six months to a year.
Both uses of finasteride highlight its role in hormonal management. It’s important for users to consult healthcare professionals before starting treatment. Regular follow-ups are recommended to monitor effectiveness and assess any potential side effects. Some common side effects include decreased libido and erectile dysfunction, though these are often temporary and may resolve after discontinuation of treatment.
In summary, finasteride serves a dual purpose in hair restoration and prostate health, making it a versatile option for men experiencing related issues. Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures safe and effective use of this medication.
Differences Between Brand Name and Generic Finasteride
Brand name and generic finasteride both serve the same purpose in treating conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia and male pattern baldness. However, they differ in several key areas, primarily in cost, appearance, and manufacturer reputation.
Cost
Generic finasteride is typically cheaper than its brand name counterpart. The reduced price stems from lower research and development costs since generics do not require the same extensive clinical trials once the original patent expires. Patients benefit significantly from this cost difference, making it more accessible.
Ingredients and Formulation
The active ingredient is the same in both formulations, finasteride, which means they exhibit the same effectiveness. However, inactive ingredients, such as fillers and coloring agents, may vary. These differences can sometimes affect tolerance or cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, so check the ingredient list if you have specific sensitivities.
Packaging and appearance also differ, as generics can vary in shape, size, and color, which may lead to confusion. Always confirm with your pharmacist if you receive a new appearance to ensure it’s the correct medication.
Both forms of finasteride are safe and effective when used as directed, but awareness of these differences empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Dosage Forms and Recommendations for Generic Finasteride
Generic finasteride is commonly available in tablet form, predominantly in doses of 1 mg and 5 mg. The choice between these dosages depends on the condition being treated. For male pattern baldness, a 1 mg dose is usually recommended, whereas, for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a 5 mg dosage is standard.
Administer the medication orally with or without food, and ensure adherence to the prescribed regimen. Patients should take finasteride at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels in the bloodstream.
When considering finasteride, consult with a healthcare provider regarding potential side effects. Users may experience decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or breast tenderness. If any severe reactions occur, seek medical advice instantly.
| Dose | Indication | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | Male Pattern Baldness | Decreased libido, erectile dysfunction |
| 5 mg | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia | Breast tenderness, ejaculation disorders |
Generic versions typically offer the same therapeutic benefits as brand-name options, making them a cost-effective choice. Check with a pharmacist to confirm the specific formulation and ensure it meets personal health needs.
Routine follow-ups with your healthcare provider allow for monitoring of progress while using finasteride. Engage in open communication regarding any concerns or side effects that arise during treatment. This proactive approach enhances safety and treatment success.
Safety, Side Effects, and Contraindications of Finasteride
Consult with a healthcare provider before starting finasteride to discuss your medical history and any current medications. Common side effects include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation disorders. These effects may persist after discontinuation in some individuals.
Less frequent side effects encompass breast tenderness or enlargement, rash, and dizziness. Rarely, serious allergic reactions such as swelling of the lips, face, or tongue may occur. If any severe side effects arise, seek immediate medical help.
Individuals with a known hypersensitivity to finasteride or any of its components should avoid its use. It’s contraindicated in pregnant women due to the risk of affecting the developing fetus. Male patients with a history of prostate cancer should also refrain from using finasteride, as its effects on prostate cancer risk remain unclear.
Regular follow-ups and monitoring of side effects are essential throughout the treatment period. Inform your doctor about any existing liver conditions, as finasteride is metabolized in the liver, which could affect the drug’s safety profile.
Discuss all potential interactions with your healthcare provider, particularly if taking medications for other conditions. This proactive approach ensures the safe use of finasteride tailored to individual health needs.
Cost Comparison: Generic versus Brand Name Finasteride
The cost of generic finasteride significantly undercuts that of its brand-name counterpart. Typically, a month’s supply of generic finasteride can range from $10 to $25, while brand-name Propecia often costs between $60 and $100 for the same duration. This substantial price difference makes the generic option a more attractive choice for many consumers.
When evaluating pharmacy prices, it’s crucial to compare various retailers. Some may offer discounts or generic alternatives that can further lower expenses. Online pharmacies might provide additional savings, but ensure they are reputable before making a purchase. Look for licensed pharmacies that require a prescription.
Insurance coverage can also affect costs. Many plans cover generic finasteride at a lower co-pay than the brand-name version. Always check with your insurance provider for the specifics of your policy, as coverage can vary widely. If you lack insurance, applying for discount cards or programs offered by pharmacies might yield additional savings.
Consider long-term costs as well. Since finasteride is frequently prescribed for ongoing use, choosing the generic variant can lead to significant savings over time. Patients often find that sticking with the generic option allows them to maintain their treatment without financial stress.
Ultimately, the cost difference between generic and brand-name finasteride plays a key role in treatment accessibility. Opting for generic finasteride can provide the same clinical benefits at a fraction of the price, making it a wise choice for budget-conscious patients.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Generic Finasteride
Generic finasteride must comply with the regulations set by the FDA or equivalent bodies in other countries. This includes demonstrating bioequivalence to the branded version, ensuring that the generic product releases the same active ingredient at the same rate and extent as the original drug.
Manufacturers need to submit an Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) to gain approval. This process requires extensive documentation, including stability data, labeling information, and manufacturing practices that meet Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Monitoring patents is crucial. Before launching a generic version, assess any remaining patents to avoid infringement. Some pharmaceutical companies may seek to extend patent protection through various strategies, including minor formulation changes or new delivery methods.
Labeling must meet specific regulatory requirements. The generic product should include all necessary information, warnings, and usage instructions in alignment with the branded drug’s labeling to ensure consumer safety and compliance.
Stay updated on market regulations, as generic medications can face challenges from pharmaceutical companies aiming to maintain market exclusivity. Participating in industry forums and discussions can help identify potential obstacles and strategies for market entry.
Finally, monitor post-marketing surveillance requirements. Even after approval, generic manufacturers must report adverse events related to their products to ensure ongoing safety and compliance with regulatory standards.