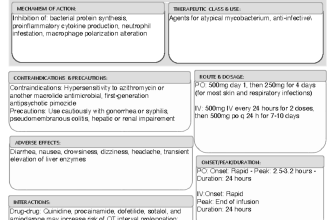
For those experiencing frequent heartburn or acid reflux, obtaining a prescription for Nexium (esomeprazole) can provide significant relief. This medication works by reducing the amount of acid the stomach produces, targeting symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other related conditions. Consult your healthcare provider to assess whether Nexium aligns with your health needs and treatment goals.
It’s essential to understand the proper dosage and duration of Nexium therapy, as both factors can vary based on individual health profiles. Generally, the typical prescription starts at 20 mg or 40 mg once daily, but your doctor may adjust this based on your specific condition. Follow your doctor’s instructions closely and communicate any side effects you may experience to ensure optimal results.
Additionally, be mindful of potential drug interactions. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter products and supplements. This information helps prevent complications and ensures that Nexium can be safely used in your treatment regimen.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will enable ongoing monitoring of your condition and allow for timely adjustments to your treatment if necessary. Taking an active role in your healthcare not only enhances the management of your symptoms but also contributes to your overall well-being.
- Drug Nexium Prescription
- Usage Guidelines
- Potential Side Effects
- Understanding Nexium: What It Is and How It Works
- How Nexium Functions
- Benefits of Nexium
- Indications for Nexium Prescription: Who Needs It?
- Dosage Guidelines for Nexium: Finding the Right Amount
- Potential Side Effects of Nexium: What to Watch For
- Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Recommendations for Monitoring
- Drug Interactions: Medications That May Affect Nexium
- Patient Considerations: Special Populations and Nexium Use
- Cautions and Warnings: When Not to Use Nexium
- Pre-existing Conditions
- Drug Interactions
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Ensuring Safe Use of Nexium
- Lab Tests and Evaluations
- Adjustment of Dosage
Drug Nexium Prescription
Nexium is commonly prescribed for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other acid-related conditions. This medication works by reducing the amount of acid the stomach produces, providing relief from symptoms such as heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and persistent cough. For adults, the typical dosage is 20 mg or 40 mg once daily, depending on the severity of the condition. For children, the dosage is based on weight and should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Usage Guidelines
Take Nexium at least one hour before meals for optimal absorption. Swallow the capsules whole; do not crush or chew them. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for the next dose, skip the missed one–do not take two doses at once. Long-term use should be monitored by a doctor due to potential risks associated with prolonged suppression of stomach acid.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include headache, nausea, and diarrhea. Report any severe reactions like chest pain, irregular heartbeat, or signs of an allergic reaction to your doctor immediately. Discuss with your healthcare provider any other medications you are taking, as Nexium can interact with certain drugs, affecting their efficacy. Regular follow-ups are recommended to assess the treatment’s effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Understanding Nexium: What It Is and How It Works
Nexium, also known as esomeprazole, belongs to a class of medications called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It effectively reduces stomach acid production, offering relief for conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcers.
How Nexium Functions
Nexium inhibits the proton pump in the stomach lining, decreasing the amount of acid released into the digestive tract. This action helps prevent damage to the esophagus and stomach lining caused by acid and promotes healing of existing ulcers.
- Dose Form: Available in delayed-release capsules and oral suspension.
- Typical Dosage: Commonly prescribed at 20 mg to 40 mg daily, depending on the condition treated.
Benefits of Nexium
- Acid Reduction: Significantly lowers stomach acid, aiding in symptom relief.
- Healing: Promotes healing of erosive esophagitis caused by reflux.
- Long-Lasting: Provides effective control of symptoms over extended periods.
Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to discuss any potential side effects, such as headache, nausea, or abdominal discomfort. Regular follow-ups may also be necessary to monitor your response to the treatment.
Indications for Nexium Prescription: Who Needs It?
Nexium is specifically prescribed for individuals diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Patients experiencing frequent heartburn or acid reflux that does not respond to over-the-counter medications often benefit from treatment with Nexium. This medication works by reducing stomach acid production, providing relief from discomfort and preventing damage to the esophagus.
Patients with erosive esophagitis caused by acid reflux may also be recommended Nexium. This condition can lead to inflammation and damage, making appropriate treatment essential for healing and symptom management.
Nexium is indicated for patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a rare condition characterized by excessive gastric acid production. Managing this condition with Nexium helps control acid levels, preventing complications and improving quality of life.
Individuals at risk for developing ulcers, particularly those taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may receive Nexium as a preventive measure. By suppressing stomach acid, the medication can help protect the gastrointestinal lining.
Lastly, patients undergoing certain stomach or esophageal surgeries might be prescribed Nexium post-operatively to aid in healing and reduce acid-related issues during recovery.
Dosage Guidelines for Nexium: Finding the Right Amount
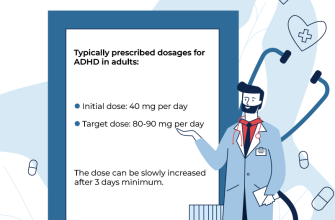
The typical starting dose of Nexium is 20 mg once daily, especially for treating conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Depending on the severity of the symptoms, doctors may adjust the dose to 40 mg once daily.
For the maintenance of GERD healing, a dose of 20 mg once daily is usually sufficient. If symptoms persist or recur, an increase to 40 mg may be recommended by your healthcare provider.
For patients suffering from Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, Nexium is prescribed at higher doses. Doses often start at 40 mg twice daily, with adjustments made based on individual response and clinical judgment.
Administer Nexium at least one hour before meals for optimal absorption. Swallow the capsule whole; do not crush or chew it. For patients who have difficulty swallowing, the contents of the capsule can be mixed with applesauce.
Monitoring is key. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will help determine if the dosage requires alteration. Always communicate any side effects or lack of improvement to adjust your treatment plan effectively.
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult their doctors for personalized advice on dosage. It is crucial to tailor the dosage based on individual health needs, conditions, and response to treatment.
Potential Side Effects of Nexium: What to Watch For
Monitor for common side effects associated with Nexium, which may include headache, diarrhea, constipation, and nausea. These symptoms are typically mild but can affect daily activities.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
Be aware of more severe reactions that require immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions: Rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or trouble breathing.
- Kidney problems: Symptoms may include decreased urination, swelling, or fatigue.
- Bone fractures: Long-term use may increase the risk of fractures, particularly in older adults.
- Low magnesium levels: Watch for muscle spasms, irregular heartbeat, or seizures.
Recommendations for Monitoring
Regular check-ups can help catch any potential issues early. Discuss any troubling symptoms with your healthcare provider. If you notice persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain or severe diarrhea, seek advice promptly.
Nexium can interact with other medications, enhancing the risk of side effects. Always inform your doctor about all the medications you take.
Consider lifestyle modifications, such as diet changes or weight management, to help reduce acid reflux symptoms without increasing reliance on medication. This proactive approach can minimize side effects and enhance overall well-being.
Drug Interactions: Medications That May Affect Nexium
Certain medications can influence the effectiveness of Nexium (esomeprazole). Be mindful of drugs like clopidogrel, which may have reduced effectiveness when taken with Nexium due to alterations in metabolism.
Antifungal medications such as ketoconazole and itraconazole rely on stomach acidity for optimal absorption. Nexium, by lowering stomach acid, can hinder their effectiveness.
Medications that reduce acid production, like HIV protease inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir), may also interact with Nexium. Atazanavir absorption can be impaired in a low-acid environment. Adjusting dosages might be necessary to maintain effectiveness.
Monitor the use of certain antibiotics, including ampicillin and amoxicillin. The absorption of these antibiotics may vary depending on stomach acidity levels influenced by Nexium.
Consult healthcare providers about potential interactions with magnesium-containing medications, as prolonged Nexium use can lead to magnesium deficiency, impacting muscle and nerve function.
Always keep a list of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, and share this with your doctor to ensure safe and effective use of Nexium.
Patient Considerations: Special Populations and Nexium Use
Patients with liver impairment may require a dosage adjustment when taking Nexium. Monitor liver function regularly, as the metabolism of the drug is affected. Start with the lowest effective dose to minimize potential risks.
For elderly patients, assess renal function before prescribing. Nexium can lead to potential kidney issues in this population, so regular monitoring of kidney health is advisable. Start treatment cautiously, considering possible polypharmacy interactions.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should only use Nexium if the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. Discuss alternatives and monitor closely if treatment is necessary. The safety profile in pregnancy is not fully established, so individualized care is key.
Pediatric patients under 12 years must be prescribed Nexium carefully. The FDA has approved it for specific conditions, so confirm the diagnosis before initiating therapy. Age-appropriate dosing is essential to avoid adverse effects.
Patients with a history of Clostridium difficile infection should discuss this with their healthcare provider, as proton pump inhibitors like Nexium may increase the risk of recurrence. Evaluate the necessity of continued use versus potential risks.
Be vigilant for drug interactions with anticoagulants, methotrexate, and other medications, which may alter the efficacy and safety of concomitant therapy. Regular reviews of the patient’s medication regimen can help mitigate these risks.
Always ensure patients are informed about potential side effects, including headaches and gastrointestinal symptoms. Encourage them to report any unusual symptoms promptly to allow for timely intervention.
Cautions and Warnings: When Not to Use Nexium
Avoid using Nexium if you have a known allergy to esomeprazole or any component of the medication. Allergic reactions can manifest as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the lips, tongue, or face. Consult a healthcare provider immediately if you experience any of these symptoms after taking Nexium.
Pre-existing Conditions
If you have a history of liver disease, inform your doctor before starting Nexium. Reduced liver function can impact how well your body processes the drug, potentially leading to increased side effects.
Avoid Nexium if you are experiencing low magnesium levels, as this medication can further lower magnesium levels in the body. Symptoms of low magnesium include muscle spasms, irregular heartbeat, and seizures. Regular monitoring of magnesium levels may be necessary during treatment.
Drug Interactions
Be cautious if you are taking certain medications, such as clopidogrel, as Nexium can reduce its effectiveness. Always disclose your full medication list to your healthcare provider to avoid harmful interactions.
Pediatric patients should not use Nexium to treat heartburn or acid reflux without the guidance of a healthcare professional, as the safety and effectiveness in this age group have not been established for these conditions.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Ensuring Safe Use of Nexium
Regular follow-up appointments are necessary while taking Nexium. Schedule visits every 3 to 6 months to review symptoms and assess the effectiveness of the treatment. During these appointments, discuss any side effects experienced and any other medications being taken.
Lab Tests and Evaluations
Monitoring for potential side effects is crucial. Your doctor may recommend periodic blood tests to check for magnesium levels, as Nexium can lead to magnesium deficiency. Review kidney function regularly to detect any impact from long-term use.
| Test | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium levels | Every 3-6 months | To monitor for deficiency |
| Kidney function | Annually | To assess any potential renal impacts |
| Bone density | Every 1-2 years | To check for osteoporosis risk in long-term users |
Adjustment of Dosage
In some cases, dosage adjustments may be necessary based on monitoring results. Discuss any concerns regarding dosage with your healthcare provider to ensure optimal safety and effectiveness. Pay attention to symptom relief, as well as the emergence of new or worsening symptoms.