Need a reliable, readily accessible Lexapro reference? Download the Davis Drug Guide PDF. This guide provides concise, clinically relevant information directly from a trusted source, streamlining your research process. You’ll find detailed prescribing information, including dosage, contraindications, and potential adverse effects, presented clearly and efficiently.
Focus on critical details: the PDF offers a structured format, allowing quick identification of key data points. Locate specific information regarding drug interactions with minimal effort. This means less time searching and more time focused on patient care. Remember to always consult with a medical professional before making any decisions regarding medication.
Key benefits include a portable format for easy access, detailed pharmacology and administration guidelines, and up-to-date information to support your clinical practice. Always verify information with the most current edition. The guide is particularly valuable for healthcare professionals requiring quick access to Lexapro’s properties.
- Lexapro Davis Drug Guide PDF: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Lexapro’s Mechanism of Action
- Navigating the Davis Drug Guide Information
- Beyond the PDF: Patient Resources
- Understanding Lexapro’s Mechanism of Action
- Indications and Approved Uses for Lexapro
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Lexapro
- Common Side Effects and Their Management
- Serious Adverse Reactions and Precautions
- Serotonin Syndrome
- Withdrawal Symptoms
- Bleeding Risk
- Interactions
- Specific Populations
- Other Precautions
- Disclaimer
- Drug Interactions with Lexapro
- Contraindications and Patient Selection
- Accessing and Interpreting the Lexapro Davis Drug Guide PDF
Lexapro Davis Drug Guide PDF: A Comprehensive Guide
Download the Lexapro Davis Drug Guide PDF directly from reputable pharmaceutical websites or your healthcare provider. This guide provides detailed information, including dosage, contraindications, side effects, and drug interactions. Always consult the most current version.
Understanding Lexapro’s Mechanism of Action
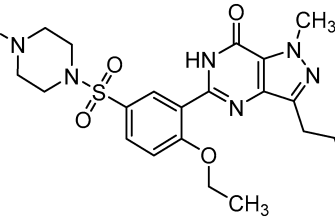
Lexapro, or escitalopram, is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It works by increasing the level of serotonin in the brain, a neurotransmitter influencing mood, sleep, and appetite. This increased serotonin helps alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Navigating the Davis Drug Guide Information
Locate sections on “Dosage and Administration” for precise instructions on how to take Lexapro. Pay close attention to “Warnings and Precautions,” identifying potential risks like serotonin syndrome or withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. Carefully review “Adverse Reactions” to understand potential side effects, ranging from mild nausea to more serious events. The “Drug Interactions” section highlights medications that could negatively affect Lexapro’s efficacy or increase adverse events. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for any questions.
Beyond the PDF: Patient Resources
While the Davis Drug Guide PDF offers valuable information, remember to discuss your treatment plan and any concerns with your healthcare professional. Supplement the PDF with information from reputable patient support organizations and your doctor’s advice for a well-rounded understanding of your medication.
Understanding Lexapro’s Mechanism of Action
Lexapro, or escitalopram, selectively inhibits serotonin reuptake in the brain. This means it increases the amount of serotonin available at nerve synapses.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter playing a key role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite. By boosting serotonin levels, Lexapro helps alleviate symptoms associated with depression and anxiety.
The drug’s selective action on serotonin, unlike some older antidepressants, minimizes impact on other neurotransmitter systems, potentially reducing side effects.
However, the precise mechanism by which increased serotonin translates to symptom relief remains an area of ongoing research. It’s believed to involve complex interactions within various brain regions and pathways.
This selective serotonin reuptake inhibition (SSRI) is the foundation of Lexapro’s therapeutic effect, offering a targeted approach to managing mood disorders.
Indications and Approved Uses for Lexapro
Lexapro (escitalopram) is primarily indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. It effectively alleviates symptoms such as persistent sadness, loss of interest, sleep disturbances, and fatigue. The FDA also approved Lexapro for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults, helping manage excessive worry and nervousness.
Beyond these primary uses, Lexapro finds application in other conditions. It’s prescribed to manage social anxiety disorder (SAD), characterized by intense fear of social situations, and panic disorder, marked by unexpected and recurrent panic attacks. Lexapro can also help alleviate the symptoms of premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), a severe form of premenstrual syndrome.
| Condition | Approved Use |
|---|---|
| Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) | Yes |
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) | Yes |
| Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) | Yes |
| Panic Disorder | Yes |
| Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) | Yes |
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or psychiatrist before starting or stopping any medication, including Lexapro. They will determine the appropriate dosage and monitor your progress. Dosage and treatment duration vary depending on individual needs and response to treatment.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Lexapro
Lexapro (escitalopram) is usually prescribed as a once-daily oral dose. Begin with a low dose and gradually increase as tolerated.
Major Depressive Disorder: The typical starting dose is 10 mg once daily. Your doctor may increase this to a maximum of 20 mg daily, depending on your response and tolerance.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Treatment usually starts at 10 mg daily. Again, your doctor can adjust this to a maximum of 20 mg daily, based on your individual needs.
- Dosage Adjustments: Changes in dosage should be made at intervals of at least one week to allow for proper assessment of response and potential side effects.
- Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
- Withdrawal: Abruptly stopping Lexapro can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will help you gradually reduce your dose to minimize these effects.
Administration: Lexapro tablets can be taken with or without food. Swallow the tablet whole; do not crush or chew it.
Important Considerations:
- Closely monitor your response to Lexapro. Report any unusual side effects to your healthcare provider.
- Inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, as interactions are possible.
- Lexapro is not suitable for everyone. Your doctor will consider your medical history and current health status before prescribing this medication.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and should not substitute advice from your doctor or other healthcare professional. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions for dosage and administration.
Common Side Effects and Their Management
Many experience nausea. Try taking Lexapro with food to minimize this. If nausea persists, contact your doctor; they may adjust your dosage or suggest an anti-nausea medication.
Drowsiness is another common side effect. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how Lexapro affects you. Gradually increasing your dosage can help mitigate this.
Some individuals report insomnia. Taking Lexapro in the morning may help. If sleep problems continue, discuss this with your healthcare provider; they may suggest adjustments to your medication schedule or recommend a sleep aid.
Sexual side effects, such as decreased libido or difficulty achieving orgasm, are possible. Open communication with your doctor is key. Alternative medications or dosage adjustments may be considered.
Headaches are relatively frequent. Staying hydrated and getting adequate rest can help. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may provide relief, but always check with your doctor before combining medications.
Weight changes (both gain and loss) have been reported. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise are crucial. Your physician can offer guidance on nutrition and physical activity if needed.
Dry mouth can be managed by drinking plenty of water and using sugar-free gum or candy. If severe, consult your physician.
Remember, these are common side effects, not everyone experiences them. Always report any concerns to your doctor or pharmacist.
Serious Adverse Reactions and Precautions
Monitor patients closely for suicidal ideation, especially during initial treatment and dosage adjustments. Report any concerning changes in behavior immediately to your prescribing physician.
Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include agitation, confusion, fever, sweating, muscle rigidity, and coordination problems. Discontinue Lexapro if you suspect serotonin syndrome.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Abruptly stopping Lexapro can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Gradually reduce your dose under your doctor’s guidance to minimize these effects. Common withdrawal symptoms include dizziness, nausea, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Bleeding Risk
- Lexapro may increase the risk of bleeding. Use caution with concurrent use of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents.
- Report any unusual bleeding or bruising to your doctor.
Interactions
Lexapro interacts with several medications. Inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This includes over-the-counter drugs. This prevents harmful interactions.
Specific Populations
- Elderly: Start with a lower dose and monitor closely for side effects.
- Children and Adolescents: Use in children and adolescents under 18 is generally not recommended unless other treatments have failed. Increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior is observed in this group.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Discuss risks and benefits with your doctor before taking Lexapro during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Other Precautions
- Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Lexapro.
- Drive carefully, as drowsiness may occur.
- Inform your doctor about any pre-existing medical conditions, especially liver or kidney disease.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician before starting, stopping, or changing any medication.
Drug Interactions with Lexapro
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, before starting Lexapro. This prevents potentially harmful interactions.
Here are some key interaction categories:
- Serotonin Syndrome Risk: Combining Lexapro with other serotonergic drugs, such as MAO inhibitors (like phenelzine or tranylcypromine), triptans (like sumatriptan), tramadol, St. John’s Wort, or lithium, significantly increases the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. Avoid concurrent use unless specifically directed by your physician.
- Increased Bleeding Risk: Lexapro, like other SSRIs, can increase bleeding risk when combined with anticoagulants (like warfarin) or NSAIDs (like ibuprofen or naproxen). Close monitoring is necessary.
- CYP450 Enzyme Interactions: Lexapro is metabolized by liver enzymes. Drugs that inhibit or induce these enzymes (CYP2C19 and CYP2D6) can affect Lexapro levels. Examples include cimetidine (inhibitor) and rifampin (inducer). Dose adjustments might be required.
- Alcohol: While not a formal contraindication, combining Lexapro with alcohol can worsen side effects like drowsiness and dizziness. Limit alcohol consumption while taking Lexapro.
Specific drug interactions vary widely, and this list isn’t exhaustive. Your doctor or pharmacist can provide personalized advice based on your individual health status and medication profile. Always consult them before making any changes to your medication regimen.
- Consult your doctor: Discuss all medications and supplements with your physician before starting Lexapro.
- Read the medication guide: The Lexapro medication guide provides details on drug interactions.
- Monitor for side effects: Pay close attention to any new or worsening symptoms while taking Lexapro.
Remember, proactive communication with your healthcare provider is key to safe medication management.
Contraindications and Patient Selection
Avoid prescribing Lexapro to patients with known hypersensitivity to escitalopram or any of its inactive ingredients. This includes individuals with a history of serious allergic reactions.
Carefully consider the risk of serotonin syndrome, especially when combining Lexapro with other serotonergic drugs. Monitor patients closely for symptoms like agitation, confusion, and hyperthermia. Discontinue Lexapro immediately if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
Use caution in patients with a history of seizures. Lexapro may lower the seizure threshold, and dose adjustments or alternative treatments might be necessary. Close monitoring is crucial.
Patients with significant hepatic impairment require dose adjustments due to reduced drug clearance. Consult the prescribing information for specific recommendations.
The following table summarizes key patient selection considerations:
| Condition | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Hypersensitivity to escitalopram or excipients | Contraindicated |
| Concurrent use of MAOIs | Avoid; allow a washout period |
| History of seizures | Use caution; monitor closely |
| Hepatic impairment | Dose adjustment needed |
| Renal impairment | Generally does not require dose adjustment |
| Pregnancy and breastfeeding | Weigh risks and benefits carefully; consider alternative treatment options |
| Elderly patients | Start with a lower dose; monitor closely for adverse effects |
Always obtain a thorough patient history, including current medications, medical conditions, and family history of mental illness. This helps determine suitability for Lexapro and minimizes the risk of adverse reactions.
Accessing and Interpreting the Lexapro Davis Drug Guide PDF
Find the Lexapro monograph within your institution’s subscription to the Davis’s Drug Guide. Many universities and hospitals provide online access; check your library resources.
If you lack institutional access, consider purchasing a personal subscription or searching reputable online pharmaceutical databases offering similar information. Be cautious of unofficial sources.
Once you locate the PDF, locate the sections detailing Lexapro’s indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, adverse reactions, drug interactions, dosage and administration, and patient counseling information. These are key areas for understanding the drug.
Pay close attention to the “Warnings and Precautions” section. This section highlights serious potential risks associated with Lexapro. Note any specific patient populations needing extra monitoring.
Review the adverse reactions thoroughly. Understand the frequency and severity of potential side effects. Learn how to recognize and manage these reactions.
The drug interaction section shows medications that might affect Lexapro’s efficacy or increase the risk of adverse effects. This is vital for safe prescribing and to avoid dangerous combinations.
Always cross-reference information in the Davis’s Drug Guide with other reputable sources such as the FDA label or other pharmacology texts to ensure accuracy and completeness before making any clinical decisions. The Davis’s Drug Guide offers a concise overview, not a replacement for broader knowledge.