Individuals seeking options for enhancing fertility often consider non-prescription Clomid. This medication, primarily used to treat ovulatory disorders, can be an accessible choice for those aiming to conceive. With Clomid available without a prescription in certain areas, understanding its use, benefits, and potential risks becomes crucial.
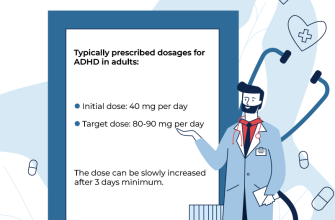
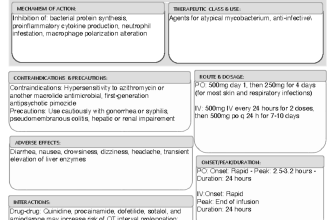
Taking Clomid without medical supervision may seem convenient, but it is essential to be aware of the appropriate dosage and timing. Generally, users begin with a standard dosage, typically 50 mg taken for five days early in the menstrual cycle. Monitoring ovulation signs, such as basal body temperature or ovulation predictor kits, aids in determining the effectiveness of the treatment.
While Clomid is well-tolerated by many, some side effects may occur, including mood swings, hot flashes, and abdominal discomfort. Recognizing these symptoms and knowing when to seek professional advice can help in managing any adverse effects. Additionally, understanding the importance of conducting a thorough fertility evaluation before starting Clomid can guide users toward making informed decisions about their reproductive health.
- Non-prescription Clomid
- Understanding the Basics of Clomid
- How Clomid Works
- Administration and Considerations
- Legality and Availability of Non-prescription Clomid
- Legal Status
- Availability
- Potential Uses of Non-prescription Clomid for Fertility
- Stimulating Ovulation
- Enhancing Fertility in Male Partners
- Dosage Guidelines for Non-prescription Clomid
- Dosage Adjustments
- Cycle Limitations
- Risks and Side Effects of Using Non-prescription Clomid
- Comparing Non-prescription Clomid with Prescription Versions
- Recommendations for Safe Use of Non-prescription Clomid
Non-prescription Clomid
Non-prescription Clomid is an option for individuals seeking assistance with ovulation regulation without the need for a doctor’s prescription. Ensure you consult reliable sources before making any decisions. Research shows that Clomid can effectively stimulate ovulation in women with certain fertility issues, especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
When considering non-prescription options, prioritize purchasing from reputable pharmacies or online retailers. Confirm that the product is genuine and adheres to safe manufacturing practices. Checking for third-party certifications can provide additional assurance that the Clomid being sold is of high quality.
Be aware of potential side effects, which include hot flashes, mood swings, and abdominal discomfort. It’s advisable to monitor your body’s response closely while using Clomid. If any severe symptoms develop, seeking medical advice is crucial.
Start with the recommended dosage, typically 50 mg per cycle, and track your ovulation patterns. Ovulation predictor kits can assist in determining the optimal time for conception.
While non-prescription Clomid offers accessible avenues for fertility support, the importance of informed use cannot be overstated. Stay educated about the medications you choose and their implications on your health. Consider consulting healthcare professionals if you have any doubts or experience challenges during the process.
Understanding the Basics of Clomid
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, serves as a medication primarily for treating female infertility. It stimulates ovulation in women who may have irregular or absent periods due to various medical conditions. By blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, Clomid prompts the pituitary gland to produce more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are crucial for ovary function.
How Clomid Works
Clomid blocks estrogen’s effects in the body, particularly in the brain. This detection of low estrogen levels leads to an increase in FSH and LH, stimulating ovarian follicles to develop and mature. Many women take Clomid during specific cycles, usually starting on the fifth day of their menstrual cycle and continuing for five days. Monitoring ovulation can be achieved using ovulation predictor kits or ultrasound examinations.
Administration and Considerations
Typically, Clomid is prescribed in a specific dosage tailored to individual needs, often starting at 50 mg per cycle. Adjustment may occur based on response and tolerance. Possible side effects include mood swings, hot flashes, and visual disturbances, but many women tolerate the medication well. While Clomid is generally safe, consulting a healthcare provider before starting is essential to address potential risks and determine suitability.
Legality and Availability of Non-prescription Clomid
Non-prescription Clomid is generally not available in most countries. This medication, primarily used to treat infertility, is classified as a prescription drug in many regions, including the United States and Europe. Accessing Clomid without a prescription may expose individuals to legal risks and potential health hazards.
Legal Status
- In the United States, Clomid requires a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider.
- European countries typically have similar regulations enforcing prescription-only availability.
- Some countries may allow over-the-counter access, but this is rare and often accompanied by specific restrictions or guidelines.
Availability
- Pharmacies across the U.S. and Europe will not dispense Clomid without a valid prescription.
- Online pharmacies may advertise non-prescription Clomid, but these sources often lack regulation and may pose serious health risks.
- Consulting a healthcare professional is the safest way to explore options related to fertility treatments, including Clomid.
Always prioritize legal channels to obtain Clomid. It ensures the medication’s authenticity and safeguards your health.
Potential Uses of Non-prescription Clomid for Fertility
Non-prescription Clomid can serve multiple roles in improving fertility outcomes. Primarily, it induces ovulation in women who have irregular menstrual cycles or anovulation. This medication stimulates the pituitary gland to release hormones that promote ovulation, significantly increasing the chances of conception.
Stimulating Ovulation
Clomid is often recommended for women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). By regulating hormone levels, Clomid helps in restoring normal ovulation patterns. Many women report success within a few cycles, which can be encouraging during their fertility journey.
The standard protocol typically involves taking Clomid for five days early in the menstrual cycle, starting on day three, four, or five. Monitoring ovulation through ultrasound or ovulation predictor kits enhances the effectiveness of this approach, ensuring timely intercourse or insemination.
Enhancing Fertility in Male Partners
Emerging evidence suggests that Clomid may also benefit male fertility. By improving testosterone levels, it can enhance sperm production. Men dealing with low sperm count or quality issues might consider Clomid as an adjunct treatment. Consulting a healthcare professional before initiating treatment is recommended to ensure appropriate dosage and monitoring.
In addition to these applications, Clomid may be an economical and accessible option for couples seeking to enhance fertility without immediate recourse to assisted reproductive technologies. Nevertheless, discussing this option with a healthcare provider ensures a tailored approach that considers individual health statuses and fertility needs.
Dosage Guidelines for Non-prescription Clomid
For non-prescription Clomid, the typical starting dosage is 50 mg taken once daily for five consecutive days, usually beginning on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle. Adjustments can be made based on individual responses and guidance from a healthcare professional.
Dosage Adjustments
If ovulation does not occur after the initial cycle, the dosage may increase to 100 mg daily for the next cycle. This adjustment should only be made under medical supervision. Do not exceed 150 mg per day, as higher doses do not consistently improve success rates and may increase potential side effects.
Cycle Limitations
Monitor your cycle for up to three treatment cycles. If pregnancy does not occur after this period, consider consulting a specialist. Regular follow-ups can help optimize your chances of conception and ensure safe use.
Risks and Side Effects of Using Non-prescription Clomid
Using non-prescription Clomid carries several risks and potential side effects that individuals should carefully consider before usage.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Clomid stimulates the ovaries, which may lead to hormonal fluctuations. These changes can cause irregular menstrual cycles or provoke symptoms of hormonal imbalance.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): This condition occurs when the ovaries respond excessively to the medication, resulting in swollen and painful ovaries. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Clomid increases the likelihood of multiple pregnancies, which comes with heightened risks for both the mother and the babies, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
- Visual Disturbances: Some users report experiencing blurred vision or other visual disturbances. This symptom can be temporary but requires prompt medical attention if it persists.
- Psychological Effects: Mood swings, anxiety, and depression may occur as a result of hormonal changes induced by Clomid. These changes can impact daily life and relationships.
Monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential if you choose to use Clomid. Regular check-ups can help mitigate risks and address side effects early.
- Consultation: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting Clomid to discuss personal health history and obtain necessary advice.
- Awareness: Be aware of your body and any changes during treatment. Report unusual symptoms to a healthcare professional promptly.
- Informed Decisions: Consider alternative fertility treatment options that might better suit individual health needs.
Staying informed and proactive in your health choices promotes safer use of Clomid and reduces associated risks.
Comparing Non-prescription Clomid with Prescription Versions
Non-prescription Clomid provides an accessible alternative for those seeking to address fertility issues. However, a direct comparison with prescription Clomid reveals key differences in regulation, usage, and efficacy.
Prescription Clomid is closely monitored by healthcare providers. Doctors typically conduct thorough evaluations to determine the appropriate dosage and monitor the patient’s response throughout the treatment. This oversight helps minimize potential side effects and ensures the medication is used effectively.
In contrast, non-prescription versions offer less guidance. Users may self-administer without professional input, which can lead to incorrect dosing or misuse. Education regarding fertility treatment becomes crucial for those opting for over-the-counter solutions.
Here’s a table summarizing the primary differences:
| Feature | Prescription Clomid | Non-prescription Clomid |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Oversight | Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional | No professional supervision |
| Dosage Control | Personalized and adjustable based on patient response | Fixed dosages prescribed by the user |
| Consultation Required | Yes | No |
| Potential Side Effects | Monitored and addressed by a doctor | May vary without professional warning |
| Efficacy Monitoring | Follow-up appointments to track effectiveness | Self-reported outcomes |
Choosing between prescription and non-prescription Clomid depends on individual circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare provider offers valuable insights and tailored recommendations, ensuring a safer path toward addressing fertility challenges.
Recommendations for Safe Use of Non-prescription Clomid
Consult a healthcare professional before starting non-prescription Clomid. This ensures it suits your health profile and personal circumstances. Your doctor can assess any potential risks and benefits based on your medical history.
Follow the recommended dosage strictly. Typically, Clomid is taken for five days, starting on the second, third, fourth, or fifth day of your menstrual cycle. Avoid exceeding the prescribed amount, as doing so may lead to adverse effects.
Monitor your body’s response while taking Clomid. Track any changes in your cycle, mood, or physical symptoms. If you notice unusual side effects, such as severe headaches or visual disturbances, contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Be aware of the potential side effects, which may include hot flashes, nausea, or mood swings. Understanding these can help you manage them more effectively and make informed decisions about further use.
Avoid taking Clomid if you are pregnant or suspect you might be. Consult a healthcare professional for advice if you think you may be expecting while using this medication.
Limit Clomid use to the recommended cycles. Extended use can lead to complications such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). If there is no pregnancy after three cycles, reassess your approach with a healthcare provider.
Consider lifestyle factors that support fertility. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and engaging in regular physical activity can enhance your overall reproductive health.
Seek support from a community or support group. Connecting with others who are on a similar path can provide encouragement and helpful insights.
Keep all medications out of reach of children and store them in a cool, dry place. Check the expiration date before use to ensure medication efficacy.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are recommended. These appointments help monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.