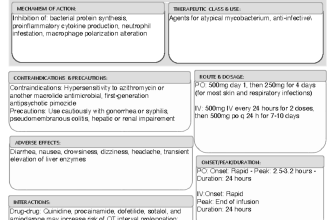
Before considering the use of non-prescription Lasix, it’s crucial to understand its implications and proper usage. Lasix, or furosemide, is a powerful diuretic that can aid in relieving fluid retention and edema. Individuals seeking over-the-counter alternatives should be cautious, as misusing this medication can lead to significant health risks.
Consulting a healthcare provider is a vital first step. They can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and existing conditions. This is especially important for those with heart or kidney issues, as diuretics can exacerbate certain ailments. Monitoring fluid intake and electrolyte levels becomes necessary to maintain health while using Lasix.
For those already familiar with diuretics, understanding dosage and frequency is key. Typically, the recommended doses vary based on individual needs. Always follow package instructions or a physician’s guidance to prevent adverse effects such as dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
Staying informed about potential side effects can enhance safety. Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and increased urination. Reporting any severe reactions to a healthcare professional can prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
By taking these precautions and seeking advice, individuals can responsibly use non-prescription Lasix to manage their health effectively.
- Non-Prescription Lasix: An Informative Guide
- Understanding Non-Prescription Lasix: Uses and Benefits
- Common Uses
- Benefits of Non-Prescription Lasix
- Potential Risks and Side Effects of Non-Prescription Lasix
- Electrolyte Imbalance
- Kidney Function
- Practical Considerations for Safe Use of Non-Prescription Lasix
Non-Prescription Lasix: An Informative Guide
Non-prescription Lasix, also known as furosemide, is primarily used as a diuretic to help reduce fluid buildup in the body. It is often employed in cases of heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disorders. Notably, it can assist in treating hypertension. Always consult with a healthcare professional before using this medication.
When considering non-prescription Lasix, one can find it in various forms, including tablets and liquid solutions. The over-the-counter version may have a lower dosage compared to prescription strength, making it important to adhere to recommended limits on the package or as directed by a pharmacist.
Side effects may include dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, or dizziness. Regular monitoring of your hydration status and electrolyte levels can prevent serious complications. Individuals with kidney issues or those on certain medications should use caution and seek medical advice before taking Lasix.
It’s important to take Lasix with a full glass of water to promote efficient absorption. Timing your intake can also be beneficial; consider taking it earlier in the day to minimize disruptions during the night due to frequent urination.
Lasix can interact with other medications, so check with a pharmacist if you are on any additional treatments. Combining diuretics with other drugs may intensify effects, leading to heightened risks or altered effectiveness.
Short-term use may be suitable for minor fluid retention, but long-term use requires monitoring to avoid dependency and maintain kidney function. Using lifestyle changes alongside Lasix, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can enhance overall health outcomes.
While non-prescription Lasix is available, understanding its uses, potential side effects, and interactions ensures safe use. Feeling uncertain? Reach out to a healthcare provider for personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding Non-Prescription Lasix: Uses and Benefits
Non-prescription Lasix, primarily known for its diuretic properties, plays a crucial role in managing certain health conditions. Individuals seeking to alleviate mild symptoms associated with fluid retention often find it beneficial. This medication encourages the kidneys to expel excess fluid, promoting a healthier balance within the body.
Common Uses
- Relief from Edema: Non-prescription Lasix is frequently utilized to reduce swelling caused by conditions such as heart failure or liver disease.
- Managing Hypertension: Some individuals take Lasix to assist in controlling high blood pressure, particularly when lifestyle changes alone fall short.
- Support During Weight Loss: People may consider it as part of a weight loss regimen, as it helps reduce water weight temporarily.
Benefits of Non-Prescription Lasix
- Accessibility: Available without a prescription, it provides easy access for those dealing with mild health issues.
- Rapid Action: Users often notice quick results, with diuretic effects typically appearing within a few hours.
- Symptom Relief: By reducing fluid retention, many experience less discomfort and improved mobility.
While Non-prescription Lasix is effective for short-term use, consulting with a healthcare provider for long-term treatment plans is advised to ensure safety and effectiveness. Always consider potential interactions with other medications and pre-existing conditions before starting any new treatment.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Non-Prescription Lasix
Using non-prescription Lasix (furosemide) carries potential risks and side effects that warrant attention. Users should consider the possibility of dehydration, which can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, dry mouth, and extreme thirst. Maintaining proper hydration is essential while using this medication.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Electrolyte imbalance is another concern, particularly with potassium levels. Low potassium (hypokalemia) may cause muscle weakness, cramps, and irregular heartbeats. Regular blood tests can monitor electrolyte levels, helping mitigate this risk.
Kidney Function
Prolonged use of Lasix can strain kidney function. Users with pre-existing kidney conditions should be cautious and consult a healthcare provider before use. Symptoms of kidney issues include changes in urine output, swelling, and fatigue that should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Allergic reactions, although rare, can occur. Signs may include rashes, itching, or swelling, especially of the face and throat. Anyone experiencing these symptoms must seek medical help promptly.
Combined with certain medications, Lasix may increase the risk of side effects. Always disclose current medications to a healthcare professional to avoid dangerous interactions. Being informed about these risks can promote safe use of non-prescription Lasix.
Practical Considerations for Safe Use of Non-Prescription Lasix
Consult a healthcare professional before starting non-prescription Lasix to ensure it’s appropriate for your health conditions. Utilize it only as directed on the label to avoid complications. Monitor your weight daily; sudden changes can indicate fluid retention or loss, signaling the need for medical attention.
Stay hydrated while using this medication, as it increases urine output which may lead to dehydration. Drinking plenty of fluids helps maintain electrolyte balance. Be mindful of dietary potassium; incorporate potassium-rich foods like bananas and leafy greens to prevent deficiency.
Set reminders to take your doses accurately; consistency enhances treatment effectiveness. Avoid combining Lasix with other medications without guidance, as interactions can raise health risks. Regularly check your blood pressure, especially if you have existing hypertension, to ensure it remains within a safe range.
Watch for side effects such as dizziness, weakness, or unusual fatigue. Report these symptoms immediately to a healthcare provider. Regular follow-ups will help assess the need for continued use and monitor any potential complications arising from the medication.
Maintain an open line of communication with your healthcare provider about any pre-existing conditions or new symptoms. Adjusting dosage or switching treatments may be necessary based on your response to Lasix.