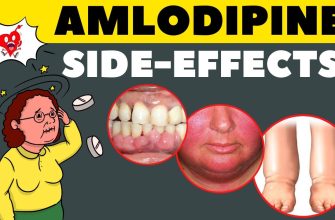
If you have been diagnosed with a fungal infection, fluconazole can be a highly effective treatment option. This antifungal medication works by inhibiting the growth of fungi, helping to alleviate symptoms and promote quicker recovery. Whether you are dealing with vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, or more severe systemic infections, fluconazole is an important ally in your treatment plan.
Dosage and administration are key to maximizing fluconazole’s benefits. For most conditions, a single dose is often sufficient, but in more severe cases, your healthcare provider may recommend a longer treatment course. Always follow your doctor’s guidelines regarding dosage and frequency to prevent potential side effects, which may include abdominal pain, nausea, or headache.
Monitoring interactions is also essential. Fluconazole can interact with various medications, notably those used for cardiovascular issues or anticoagulants. Discuss all current medications with your healthcare provider to avoid complications. Staying informed will help ensure the safe and effective use of fluconazole, supporting your overall health recovery journey.
Prescription Drugs: Fluconazole
Fluconazole is commonly prescribed to treat fungal infections, including candidiasis and cryptococcal meningitis. If you’re starting fluconazole, follow these key recommendations to ensure optimal results.
- Dosage: Adhere to the healthcare provider’s prescribed dosage. Typical doses range from 150 mg for a single dose in candidiasis to higher daily doses for more severe infections.
- Administration: Take fluconazole with or without food. Consistency in how you take the medication helps maintain stable drug levels in your body.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water while on fluconazole. Adequate hydration supports kidney function and medication clearance.
Monitor your body’s response during treatment. Both common and serious side effects can arise.
- Common side effects: These may include nausea, headache, and dizziness. Report persistent or worsening symptoms to your healthcare provider.
- Serious side effects: Look out for signs of liver problems, such as jaundice, or severe skin reactions. Seek medical attention immediately if these occur.
Inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you’re taking. Some drugs may interact with fluconazole, altering its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects.
Complete the full course of fluconazole as prescribed for fungal infections. Stopping treatment early can lead to the infection returning or worsening.
Consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or experience unusual symptoms. Regular follow-ups can help track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Mechanism of Action and Indications for Fluconazole Use
Fluconazole works primarily by inhibiting the enzyme lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, a key player in the synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. This action disrupts the integrity of the cell membrane, leading to increased permeability and ultimately the death of the fungal cell. Fluconazole’s selective targeting of fungal cells, coupled with minimal impact on human cells, contributes to its safety profile.
This medication is particularly effective against Candida species, including Candida albicans, and certain Cryptococcus species. It’s commonly prescribed for the treatment of candidiasis, including oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis. Fluconazole is also indicated for the management of cryptococcal meningitis, especially in patients with HIV/AIDS. Prophylactic use in immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or at risk for invasive fungal infections, is another key indication.
Due to its favorable pharmacokinetics, fluconazole has a wide distribution in body fluids, including cerebrospinal fluid, making it suitable for treating central nervous system infections. It can be administered orally or intravenously, allowing flexibility based on patient needs.
When considering fluconazole, assess patient-specific factors such as renal function, as dosage adjustments may be necessary. Regular monitoring can help manage potential adverse effects, particularly in those on multiple medications that may interact with fluconazole.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Considerations for Fluconazole
The standard oral dosage for treating most fungal infections in adults typically begins at 150 mg for a single dose when targeting vaginal candidiasis. For more severe infections like systemic candidiasis or cryptococcal meningitis, the dosage often increases to 400-800 mg on the first day, followed by 200-400 mg daily. Adjust dosing based on the patient’s response and the specific type of infection.
Always tailor the dosage for patients with renal impairment. For those with creatinine clearance ≤50 mL/min, consider reducing the dose or extending the interval between doses. Monitor renal function closely during therapy.
Fluconazole can be administered with or without food, allowing for flexibility in the patient’s routine. For oral suspension, ensure proper shaking before dosing to achieve uniform distribution. Dosing may be adjusted based on the desired therapeutic outcome and tolerance.
While generally regarded as safe, be aware of potential interactions with other medications. Strong CYP450 inhibitors, such as certain antibiotics and antifungal agents, may elevate fluconazole levels in the bloodstream, necessitating close monitoring and possible dosage adjustments.
Pregnant individuals should consult a healthcare provider since fluconazole can cross the placenta and may have implications for fetal health, particularly at higher doses. Always assess the risk versus benefit of therapy in such cases.
Regular follow-up appointments can help evaluate treatment effectiveness and manage any adverse effects. Encourage patients to report any unusual symptoms or concerns during their treatment.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Fluconazole
Fluconazole may cause several side effects, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, and abdominal pain. Skin reactions, such as rash or itching, can also occur. In rare cases, serious effects like liver damage or severe allergic reactions may manifest. Monitor for any unusual symptoms and consult a healthcare provider if they arise.
Drug interactions are significant when taking fluconazole. It can increase the levels of certain medications, leading to heightened effects or toxicity. Medications like warfarin and certain antihistamines may react. Always inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, prior to starting fluconazole. Adjustments may be necessary to ensure safety and efficacy.
Patients with pre-existing conditions, particularly liver issues, should use fluconazole with caution. Regular liver function tests are advisable during treatment. Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidelines regarding dosage and duration of therapy.