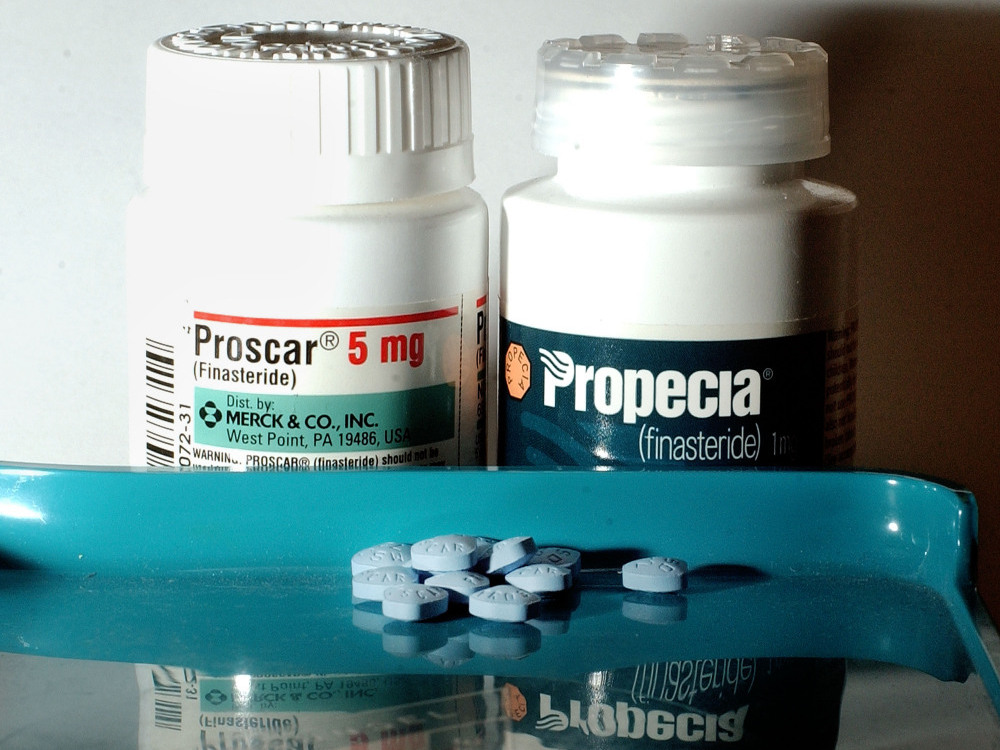
For those facing the challenges of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or male pattern baldness, prescription finasteride can offer significant benefits. This medication works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to prostate enlargement and hair loss. Regularly using finasteride can lead to a notable decrease in prostate size, improving urinary flow and reducing discomfort associated with BPH.
Consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosages and evaluate your specific health needs. Studies suggest that a daily dose of 5 mg may effectively manage BPH symptoms, while 1 mg has shown effectiveness in treating hair loss. Understanding potential side effects, like sexual dysfunction, will help you weigh the medication’s benefits against its risks.
Incorporating finasteride into your treatment plan requires an informed discussion with your doctor about your medical history and any other medications you may be taking. Regular follow-ups can help monitor progress and adjust dosages if necessary. By actively managing your health, you can experience improvements in quality of life and regain confidence in your appearance.
- Understanding Prescription Finasteride for Prostate Health
- Mechanism of Action: How Finasteride Works in Prostate Treatment
- Impact on Hormone Levels
- Clinical Outcomes
- Dosage Recommendations and Administration Guidelines for Finasteride
- Administration Tips
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Potential Side Effects and Considerations for Patients on Finasteride
- Monitoring and Communication
- Health Risks and Precautions
- Comparative Effectiveness: Finasteride in Relation to Other Prostate Treatments
- Comparison with Alpha-Blockers
- Comparison with Surgical Options
Understanding Prescription Finasteride for Prostate Health
Prescription finasteride effectively reduces prostate size in men experiencing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It works by inhibiting the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to prostate growth.
This medication typically allows for decreased urinary symptoms such as difficulty in starting urination, weak flow, and the need to urinate frequently at night. Research shows that finasteride can halve the risk of surgery and other complications associated with BPH.
Dosage recommendations vary, but the standard approach involves taking a 5 mg tablet once daily. It’s advisable to discuss individual health conditions with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Benefits of finasteride include:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduction in Symptoms | Improved urinary flow and reduced frequency of urination. |
| Prostate Size | Decrease in prostate volume, minimizing discomfort. |
| Complication Prevention | Lower risk of developing more severe complications requiring surgery. |
Potential side effects may include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and breast tenderness. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring any adverse reactions.
In conclusion, finasteride presents a viable option for managing BPH symptoms, promoting better prostate health through hormonal balance. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Mechanism of Action: How Finasteride Works in Prostate Treatment
Finasteride effectively reduces the size of an enlarged prostate by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to prostate enlargement. By blocking this conversion, finasteride lowers DHT levels, leading to decreased prostate volume and alleviation of urinary symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Impact on Hormone Levels
Finasteride specifically targets the type II 5-alpha-reductase isoenzyme, predominantly found in prostate tissue. This selective inhibition helps maintain testosterone levels while significantly reducing DHT. As a result, patients may experience improvements in urinary flow and a decrease in the frequency of nighttime urination.
Clinical Outcomes
Clinical studies demonstrate that finasteride therapy results in a marked reduction of prostate size and improvement in patients’ quality of life. Regular use of finasteride can help prevent complications such as acute urinary retention and the need for surgical intervention. With proper guidance, patients can manage their symptoms effectively and enhance their overall prostate health.
Dosage Recommendations and Administration Guidelines for Finasteride
The recommended dose of finasteride for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is 5 mg taken once daily. It is important to take the medication at the same time every day to maintain consistent blood levels. For male pattern hair loss, a dosage of 1 mg daily is advised. Adjusting the dosage is not necessary, and taking more than the prescribed amount will not increase efficacy and may lead to an uptick in side effects.
Administration Tips
Swallow finasteride tablets whole with a glass of water. You can take them with or without food. Do not crush or chew the tablets, as this can alter the medication’s effectiveness. Consistency in timing and routine will contribute to the best results in your treatment.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients taking finasteride should be aware of possible side effects, which may include sexual dysfunction, mood changes, and allergic reactions. Sexual side effects often manifest as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or ejaculation disorders. These symptoms may resolve after discontinuation, but some individuals report persistence. Open communication with your healthcare provider about any changes is essential for effective management.
Monitoring and Communication
Regular monitoring is crucial. Schedule follow-up appointments to assess prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels and discuss any emerging side effects. Some men experience mood alterations, including depression or anxiety, while taking finasteride. Reporting these changes is important, as adjusting dosage or exploring alternative treatments may be necessary.
Health Risks and Precautions
Be aware of potential health risks, including the possibility of breast tenderness or lumps. While rare, these conditions warrant immediate evaluation. Men considering fatherhood should consult their healthcare provider, as finasteride may affect sperm viability. It is essential to understand these considerations, as they play a significant role in treatment decisions.
Comparative Effectiveness: Finasteride in Relation to Other Prostate Treatments
Finasteride offers a potent solution for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern hair loss. It effectively reduces prostate volume and alleviates urinary symptoms, often leading to a notable improvement in quality of life for patients.
Comparison with Alpha-Blockers
Alpha-blockers like tamsulosin provide immediate relief from urinary symptoms by relaxing the bladder neck and prostate muscles. However, they do not reduce prostate size. Finasteride demonstrates its advantage in long-term management by targeting the underlying issue–prostate enlargement. A combination therapy using both finasteride and an alpha-blocker often yields superior outcomes compared to either treatment alone, making it a common recommendation for patients with significant BPH symptoms.
Comparison with Surgical Options
While surgical interventions, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), offer immediate relief, they carry risks of complications and longer recovery times. Finasteride, being non-invasive, presents a safer alternative, particularly for those who wish to avoid surgery. Clinical studies indicate that many men achieve satisfactory results with finasteride alone, delaying or even avoiding the need for surgery.
- Finasteride and alpha-blockers together improve urinary flow more effectively than either alone.
- Finasteride reduces surgical intervention needs in many patients.
- Finasteride has a favorable safety profile compared to surgical methods.
Patients considering prostate treatment should discuss their options thoroughly, weighing the benefits of finasteride against other therapies. Regular monitoring and follow-up consultations ensure that the chosen treatment remains effective and tailored to individual needs.