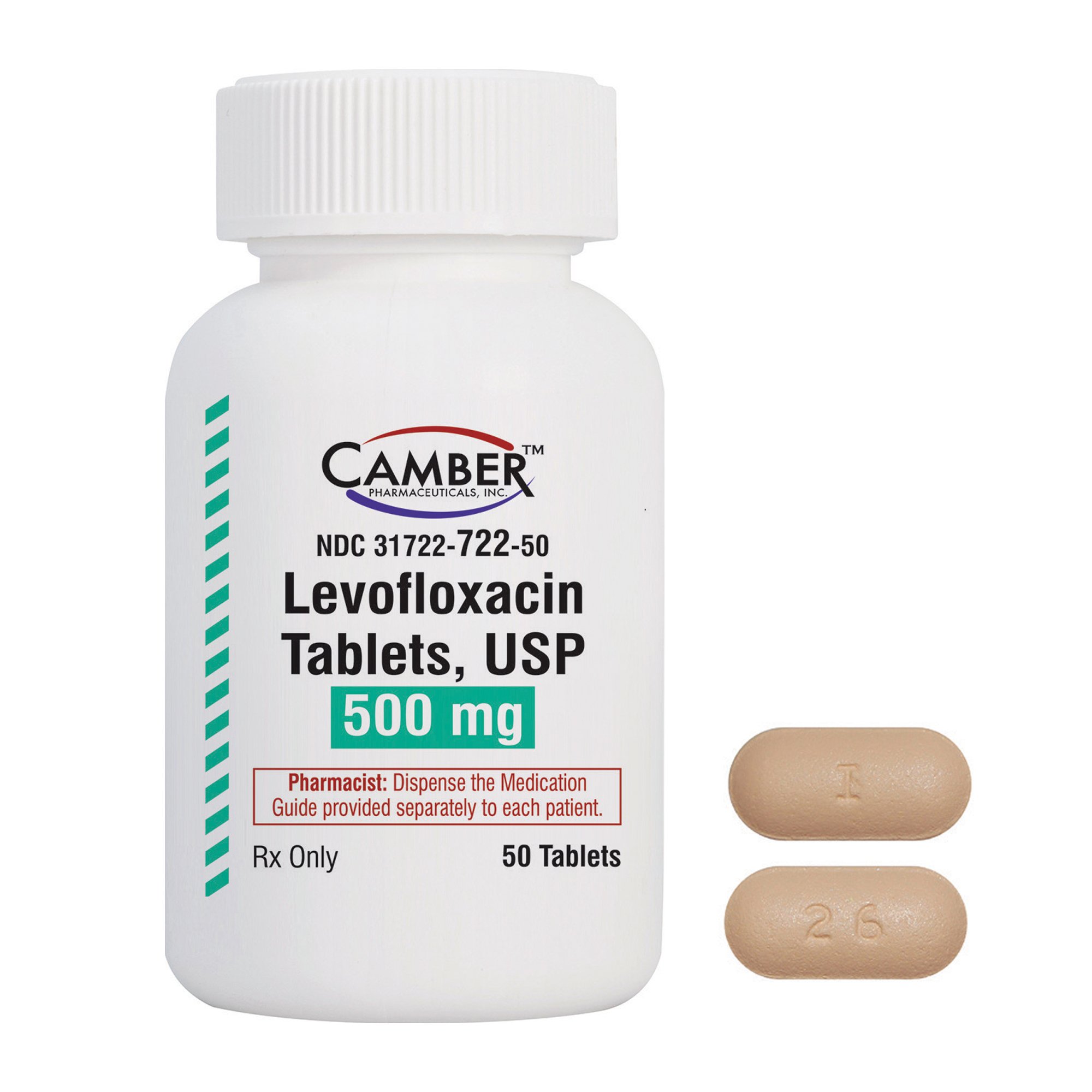
Levaquin, a widely prescribed medication, effectively treats various bacterial infections. Physicians often recommend it for conditions such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. Understanding its proper use can significantly improve your treatment outcomes.
This fluoroquinolone antibiotic works by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication, stopping the infection from spreading. Patients typically take Levaquin orally, following a dosage plan tailored to their specific medical needs. It’s essential to complete the full course, even if symptoms improve before finishing all doses.
Side effects can occur, including nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness. If you experience severe reactions, such as tendon pain or mood changes, contact a healthcare provider immediately. Always inform your doctor about your medical history and any concurrent medications to avoid potential interactions.
Levaquin may interact with certain supplements or medications, notably antacids containing magnesium or aluminum. Taking these at different times can enhance absorption and efficacy. Staying hydrated while on this medication also aids in preventing side effects and ensures proper kidney function.
- Prescription Levaquin: A Comprehensive Guide
- Usage and Dosage
- Side Effects and Precautions
- What is Levaquin and its Active Ingredient?
- Indications for Prescribing Levaquin
- Respiratory Infections
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Proper Dosage and Administration of Levaquin
- Common Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Drug Interactions: What to Watch Out For
- Precautions and Contraindications for Levaquin Users
- Frequently Asked Questions about Prescription Levaquin
Prescription Levaquin: A Comprehensive Guide
Levaquin, generically known as levofloxacin, is a widely prescribed antibiotic that effectively treats various bacterial infections. This medication belongs to the fluoroquinolone class, which targets specific types of bacteria. If your healthcare provider prescribed Levaquin, it is crucial to follow their instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
Usage and Dosage
Levaquin is commonly used to treat respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. Dosage typically ranges from 250 mg to 750 mg, depending on the type and severity of the infection. Always take the medication exactly as directed, and do not skip doses or stop early, even if symptoms improve. Full adherence to the prescribed course reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Side Effects and Precautions
Possible side effects include nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, and headache. More severe reactions, though rare, can involve tendon damage or central nervous system effects. Inform your doctor about any pre-existing conditions, especially kidney problems or a history of seizures. Stay hydrated while using Levaquin, as this can help mitigate some potential side effects.
If you experience severe headaches, confusion, or unusual thoughts, seek medical attention immediately. Avoiding this medication if you are pregnant or breastfeeding is recommended, as it may pose risks to the fetus or infant.
What is Levaquin and its Active Ingredient?
Levaquin is a prescription medication used for treating various bacterial infections. The active ingredient in Levaquin is levofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. This medication works by interfering with the bacterial DNA replication process, ultimately killing the bacteria responsible for the infection.
Levofloxacin is effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, making it a choice for conditions such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. It is crucial to use Levaquin only for infections confirmed to be bacterial to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Dosage and duration depend on the type and severity of the infection. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for optimal results. Be aware of potential side effects, which include nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness. If you experience unusual symptoms or signs of an allergic reaction, contact your doctor immediately.
Levaquin may interact with other medications, so share your complete medical history with your healthcare provider. Proper hydration is also recommended while taking this medication to help reduce the risk of certain side effects, especially those affecting the kidneys.
Indications for Prescribing Levaquin
Levaquin, or levofloxacin, is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections. It effectively targets respiratory, urinary tract, and skin infections. When encountering pneumonia, healthcare providers recommend Levaquin as a suitable treatment option due to its broad-spectrum efficacy against common pathogens.
Respiratory Infections
For patients presenting with community-acquired pneumonia or acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, Levaquin is a strong choice. Its ability to penetrate lung tissue ensures effective treatment against pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
Urinary Tract Infections
Levaquin is also indicated for uncomplicated and complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis. It demonstrates a high success rate in eradicating Escherichia coli, a common culprit in such infections.
In summary, Levaquin serves as a versatile antibiotic for treating a range of bacterial infections, particularly in respiratory and urinary tract scenarios. Always consult a healthcare professional to confirm the appropriateness for individual cases.
Proper Dosage and Administration of Levaquin
Administer Levaquin according to your doctor’s prescription. The typical dosage ranges from 250 mg to 750 mg once daily, depending on the infection being treated. For most infections, a 500 mg dose is common.
Take Levaquin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after ingesting antacids, vitamins, or supplements containing iron or zinc. This ensures optimal absorption. Swallow the tablet whole with a full glass of water.
To maintain effectiveness, adhere to the prescribed schedule, even if you start feeling better. Completing the full course eliminates the risk of antibiotic resistance. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, but skip it if it’s almost time for your next dose.
Factors like age, kidney function, and specific health conditions can influence your dosage. Always inform your healthcare provider about your medical history to tailor the most appropriate treatment plan.
For those with kidney issues, dosage adjustments are critical. Regular monitoring and consultation with your doctor will help manage your treatment safely.
Stay hydrated while on this medication. Drinking enough fluids supports kidney function and decreases the risk of side effects.
If you experience any severe side effects, such as tendon pain or rash, seek medical attention immediately. Clear communication with your healthcare team ensures safe usage of Levaquin and promotes recovery.
Common Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Levaquin can cause several side effects. It is important to monitor your health closely while on this medication.
- Gastrointestinal issues:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- CNS effects:
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Insomnia
- Skin reactions:
- Rash
- Itching
- Photosensitivity
- Musculoskeletal concerns:
- Tendinitis
- Tendon rupture
- Cardiovascular issues:
- Prolonged QT interval
- Arrhythmias
If you notice severe side effects, including abdominal pain, joint pain, or shortness of breath, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Stay hydrated and monitor for signs of allergic reactions, such as swelling or difficulty breathing. Early intervention can prevent complications.
Drug Interactions: What to Watch Out For
Levaquin can interact with various medications, impacting their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Always inform your healthcare provider of all medications you use, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid complications.
Pay special attention to the following drug interactions:
| Drug | Interaction Type | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Antacids | Reduced absorption of Levaquin | Separate doses by at least 2 hours. |
| Warfarin | Increased bleeding risk | Monitor INR levels closely and adjust dosage if necessary. |
| Corticosteroids | Increased risk of tendon rupture | Discuss alternatives with your doctor. |
| Diabetes medications | Potential for altered blood sugar levels | Regularly check blood glucose levels during treatment. |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Higher risk of CNS effects | Avoid using together unless directed by a physician. |
Monitor for any unusual symptoms and communicate them to your healthcare provider. Regular follow-ups help ensure safe and effective management of your treatment plan.
Precautions and Contraindications for Levaquin Users
Before taking Levaquin, discuss any existing medical conditions with your healthcare provider. It is crucial to disclose if you have a history of:
- Allergic reactions to levofloxacin or similar antibiotics.
- Tendinitis or tendon rupture, especially if you are over 60 years old.
- Kidney problems, as dosage adjustments may be necessary.
- Myasthenia gravis, as this medication may worsen muscle weakness.
Patients should avoid this medication if they are pregnant or breastfeeding, as potential risks to the fetus or infant exist. Consult your doctor for safer alternatives.
Monitor for side effects such as:
- Severe dizziness or fainting.
- Unusual joint or muscle pain.
- Signs of an allergic reaction, including rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Neurological effects such as confusion or hallucinations.
Always avoid consuming antacids and supplements containing magnesium, aluminum, or iron within two hours before or after taking Levaquin, as they can inhibit absorption.
For individuals with diabetes, careful monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential, as Levaquin can cause fluctuations. Be vigilant in assessing any sudden changes.
Consult your healthcare provider if you are taking other medications, including:
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin).
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen).
- Corticosteroids, which may increase the risk of tendon damage.
Adhering to these guidelines helps ensure safe usage of Levaquin, minimizing potential risks and enhancing treatment efficacy.
Frequently Asked Questions about Prescription Levaquin
Levaquin is an antibiotic prescribed to treat various bacterial infections. Ensure to take it exactly as directed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or stopping treatment early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Common side effects of Levaquin include nausea, diarrhea, headache, and dizziness. If you experience severe side effects, such as tendon pain or unusual mental health changes, contact your doctor immediately.
It’s important to inform your doctor about your complete medical history, especially if you have a history of tendon problems, seizures, or heart issues. Certain medications may interact with Levaquin, so disclose all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Your doctor will usually recommend avoiding dairy and antacids within two hours of taking Levaquin. These substances can hinder absorption, making the medication less effective.
Alcohol can increase the risk of side effects, so it’s wise to limit or avoid alcohol consumption while taking this medication.
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult their healthcare provider before starting Levaquin, as the effects on the fetus or infant are not fully understood.
To enhance recovery, maintain hydration and follow a balanced diet while on Levaquin. If you have additional questions or concerns about your treatment, reach out to your healthcare provider for personalized advice.