Consider this: Viagra, famously known for treating erectile dysfunction, also shows promise in boosting athletic performance. Studies suggest improved oxygen delivery to muscles, potentially leading to increased stamina and endurance. This isn’t about creating superhuman athletes; it’s about understanding a drug’s multifaceted effects.
Recent research highlights the mechanism behind this. Viagra’s primary action involves relaxing blood vessels. This improved blood flow isn’t limited to the genitals; it affects the entire circulatory system. The resulting enhanced oxygen transport can significantly benefit athletes in endurance sports like cycling or long-distance running.
However, it’s crucial to emphasize the ethical and legal implications. Using Viagra without a prescription for performance enhancement is prohibited in most competitive sports. Furthermore, potential side effects, ranging from headaches to vision disturbances, must be considered. Consult a physician before considering Viagra for any purpose, especially athletic enhancement. Safe and responsible use is paramount.
- Viagra as a Performance Enhancing Drug
- Cardiovascular Effects
- Limitations and Risks
- Scientific Evidence and Research
- Summary of Key Findings
- Consult a Physician
- Viagra’s Mechanism of Action and Vascular Effects
- Nitric Oxide’s Role
- Vascular Effects Beyond the Penis
- Viagra’s Impact on Endurance and Physical Performance
- Viagra and Athletic Performance: Evidence and Studies
- Potential Mechanisms and Limited Evidence
- Side Effects and Risks
- Conclusion: No Proven Performance Enhancement
- The Risks and Side Effects of Viagra Use in Athletes
- Viagra’s Use in Specific Sports and Disciplines
- Ethical Considerations and the Ban on Viagra in Sports
- Legal Status of Viagra as a Performance Enhancer
- Sports and Competition
- Other Contexts
- Alternatives to Viagra for Performance Enhancement
Viagra as a Performance Enhancing Drug
Viagra, primarily known for treating erectile dysfunction, has garnered attention for its potential performance-enhancing effects in specific athletic contexts. Its impact is complex and not universally applicable.
Cardiovascular Effects
Some studies suggest Viagra might improve cardiovascular performance by dilating blood vessels, increasing blood flow to muscles. This could theoretically lead to enhanced endurance in certain situations. However, this effect is limited and heavily dependent on individual factors such as pre-existing cardiovascular health. Using Viagra for this purpose is risky without medical supervision.
Limitations and Risks
The use of Viagra as a performance enhancer is highly discouraged. The drug’s effects are unpredictable and can interact negatively with other medications. Side effects, ranging from headaches and flushing to more serious cardiovascular complications, are possible. Furthermore, many sporting organizations explicitly prohibit its use.
Scientific Evidence and Research
Currently, the scientific evidence supporting Viagra as a broadly effective performance enhancer in athletics is weak and inconclusive. More robust, controlled studies are needed before any definitive conclusions can be drawn. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Summary of Key Findings
| Aspect | Observation |
|---|---|
| Potential Benefit | Improved blood flow, potentially enhancing endurance in specific scenarios. |
| Limitations | Limited evidence, unpredictable effects, significant risks, and potential for negative interactions with other medications. |
| Regulatory Status | Prohibited by many sports organizations. |
Consult a Physician
Always consult a medical professional before considering Viagra, even for non-sexual performance enhancement. A doctor can assess your individual health status and determine if it’s safe and appropriate for you.
Viagra’s Mechanism of Action and Vascular Effects
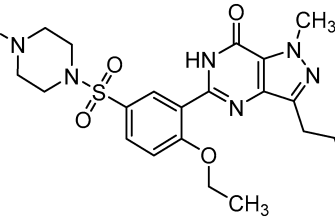
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This enzyme breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a crucial molecule for smooth muscle relaxation. By blocking PDE5, Viagra increases cGMP levels. Higher cGMP levels lead to relaxation of smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, allowing increased blood flow. This improved blood flow is the key to achieving and maintaining an erection.
Nitric Oxide’s Role
The process begins with the release of nitric oxide (NO). NO activates an enzyme called guanylate cyclase, which then produces cGMP. Viagra enhances the effects of NO by prolonging cGMP’s action. This synergistic relationship between NO and cGMP is fundamental to Viagra’s mechanism. Therefore, adequate NO production is necessary for Viagra to be effective.
Vascular Effects Beyond the Penis
While primarily known for its effects on penile blood vessels, Viagra also impacts other vascular systems. It can cause vasodilation, widening blood vessels throughout the body. This can lead to side effects such as headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion. These effects highlight Viagra’s broader impact on the circulatory system. Clinicians should carefully consider these broader vascular effects when prescribing the drug.
Viagra’s Impact on Endurance and Physical Performance
Viagra, while primarily known for treating erectile dysfunction, has shown some influence on endurance and physical performance in specific contexts. Studies suggest it may improve exercise capacity in individuals with pulmonary hypertension, a condition affecting blood vessels in the lungs, by improving blood flow. This improvement translates to potentially increased stamina during physical activity. However, these findings are not directly transferable to healthy individuals without pulmonary hypertension. Expect minimal to no impact on endurance for people without this condition.
Some studies have explored Viagra’s effects on muscle function and blood flow during exercise in healthy individuals. While some small enhancements have been observed, the results are generally inconclusive and often vary widely depending on dosage and individual factors like age and baseline fitness level. These marginal gains, if any, may not be significant enough to justify its use for performance enhancement in healthy athletes.
Crucially, using Viagra for non-medical purposes carries risks. Side effects, including headaches, flushing, and visual disturbances, are possible. More serious side effects, though rare, also exist. Consult a physician before considering Viagra for any non-approved use; they can assess your health and discuss safer alternatives for enhancing athletic performance.
In summary, the evidence supporting Viagra as a performance-enhancing drug for endurance is limited, mainly restricted to specific medical conditions like pulmonary hypertension. For healthy individuals seeking improved athletic performance, focusing on proper training, nutrition, and adequate rest remains far safer and more effective.
Viagra and Athletic Performance: Evidence and Studies
Current research suggests Viagra (sildenafil) doesn’t directly enhance athletic performance in the way performance-enhancing drugs like steroids do. Studies haven’t shown significant improvements in strength, endurance, or speed.
Potential Mechanisms and Limited Evidence
Some speculate sildenafil might indirectly improve performance by increasing blood flow to muscles. However, studies exploring this are limited and inconclusive. The few existing trials show minimal effects, and more robust, large-scale research is necessary.
- One small study suggested potential benefit in high-altitude athletes, but findings remain questionable due to study limitations.
- Other studies have focused on specific athletic populations, such as cyclists, with no definitive results showing performance enhancement.
Side Effects and Risks
Using sildenafil without a prescription carries significant health risks. Possible side effects include:
- Headache
- Facial flushing
- Visual disturbances
- Low blood pressure
- Heart problems
These risks outweigh any potential, currently unproven, performance benefits. Consult a physician before using any medication, including sildenafil, for athletic enhancement.
Conclusion: No Proven Performance Enhancement
There’s currently no reliable scientific evidence supporting sildenafil as a performance-enhancing drug for athletes. The potential risks associated with its use far outweigh any theoretical benefits.
- Seek medical advice before using any medication for athletic purposes.
- Focus on proven training methods and healthy lifestyle choices for performance improvement.
The Risks and Side Effects of Viagra Use in Athletes
Avoid Viagra for performance enhancement. Its cardiovascular effects pose significant dangers for athletes, especially during strenuous activity. Increased heart rate and blood pressure, common side effects, can strain the heart and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Viagra also interacts negatively with some commonly used performance-enhancing drugs and supplements, potentially causing unpredictable and hazardous reactions. This includes an increased risk of hypotension (low blood pressure).
Muscle pain, headaches, and visual disturbances are frequent side effects that can impair athletic performance and training. These effects can significantly impact an athlete’s ability to train effectively and compete at their best.
Long-term Viagra use can lead to vision problems, hearing loss, and priapism (a prolonged, painful erection). These conditions necessitate immediate medical attention and can have long-lasting consequences for athletes.
Consult a physician before considering any medication for performance enhancement. There are safer and more appropriate methods for improving athletic performance, and a doctor can help you find the right strategy for your needs.
Viagra’s Use in Specific Sports and Disciplines
While Viagra isn’t directly a performance enhancer in the way steroids are, its effects on blood flow and potentially endurance have led to speculation regarding its use in specific sports. Let’s examine some areas where its potential impact has been discussed.
- Endurance Sports: Some athletes in endurance sports, such as cycling and long-distance running, might hypothetically use Viagra to improve blood flow to muscles, potentially boosting stamina. However, scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited, and any performance enhancement is likely minimal and highly variable. The risks associated with Viagra outweigh any theoretical benefits.
- High-Altitude Sports: The reduced oxygen availability at high altitudes can impair athletic performance. Viagra’s theoretical ability to improve blood oxygenation has led to discussion of its possible use in mountain climbing or high-altitude skiing. Again, rigorous scientific backing is lacking, and the safety concerns remain considerable.
- Weightlifting and Strength Training: No credible evidence supports Viagra improving muscle strength or growth directly. Its potential vascular effects are not linked to improved muscle protein synthesis or hypertrophy.
- Combat Sports: No evidence exists to support a performance-enhancing role for Viagra in combat sports like boxing or mixed martial arts. Its effects are not relevant to factors determining success in these disciplines such as speed, power, or agility.
It’s crucial to note that using Viagra for athletic enhancement is highly discouraged. The potential side effects, including cardiovascular complications, significantly outweigh any potential, unproven benefits. Athletes should prioritize safe and ethical training practices. Always consult a physician before using any medication, especially in the context of athletic training.
- Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Ethical Considerations and the Ban on Viagra in Sports
The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) prohibits Viagra (sildenafil) because it enhances blood flow, potentially boosting athletic performance, particularly in endurance events. This raises fairness concerns: athletes using Viagra gain an unfair advantage over those who don’t.
Beyond fairness, Viagra’s cardiovascular effects present health risks. Increased blood pressure and potential heart complications could seriously endanger athletes, especially during strenuous competition. WADA’s ban aims to protect athlete well-being.
The ban’s implementation presents challenges. Detecting Viagra use requires sophisticated testing, and some athletes might use it off-label for conditions unrelated to performance enhancement. Clear guidelines are needed to differentiate legitimate medical use from doping.
Ethical discussions also encompass the potential for coercion. Pressure from coaches or teammates could lead athletes to use Viagra against their better judgment. Educational programs promoting responsible athletic conduct and respecting individual choices are vital.
Finally, the ban’s effectiveness hinges on consistent enforcement and transparency. Regular testing and readily available information regarding WADA’s rules ensure athletes understand the consequences of using prohibited substances, preventing unintended violations.
Legal Status of Viagra as a Performance Enhancer
Viagra’s legal status as a performance enhancer is complex and varies considerably depending on context and jurisdiction. In most countries, Viagra (sildenafil) requires a prescription for its use in treating erectile dysfunction. Using it without a prescription is illegal.
Sports and Competition
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) regulations prohibit sildenafil’s use in sports competition. This is because it can improve athletic performance indirectly by enhancing blood flow to muscles, potentially boosting stamina and endurance. Athletes found using sildenafil without a therapeutic use exemption face sanctions. However, WADA’s focus is primarily on the competitive advantage, not the inherent illegality of the drug itself.
Other Contexts
Outside of sports, legal ramifications for using Viagra without a prescription primarily revolve around obtaining the drug illegally. This could involve purchasing it from unauthorized sources online or otherwise circumventing prescription requirements. Penalties vary but might include fines or other legal consequences. Consult your physician for appropriate use and obtain prescriptions legitimately.
Alternatives to Viagra for Performance Enhancement
Consider lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and stress reduction techniques like yoga or meditation can significantly improve blood flow and overall health, positively impacting sexual performance.
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors other than Viagra: Cialis and Levitra offer similar benefits but with different durations of effect. Consult your doctor to determine which medication best suits your needs and health profile.
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT): Low testosterone levels contribute to erectile dysfunction. If your doctor confirms low testosterone, TRT may be a viable option, but it requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
Vacuum erection devices: These devices create a vacuum around the penis to help achieve an erection. They’re a non-invasive option suitable for some men, though they may not be comfortable for everyone.
Penile implants: These surgically implanted devices offer a permanent solution for erectile dysfunction, providing rigidity for sexual intercourse. This is a more invasive option and should only be considered after exhausting less-invasive treatments.
Counseling: Addressing underlying psychological issues like performance anxiety or relationship problems through therapy can be highly beneficial for improving sexual performance.
Always consult a healthcare professional: Before starting any new treatment, discuss your options with a doctor. They can assess your individual circumstances and recommend the most appropriate and safe approach for performance enhancement.