When considering a prescription for Levaquin, it’s crucial to evaluate the patient’s specific condition. Levaquin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, is effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory and urinary tract infections. Ensure that the diagnosis accurately reflects the need for this medication, as it is not suitable for viral infections.
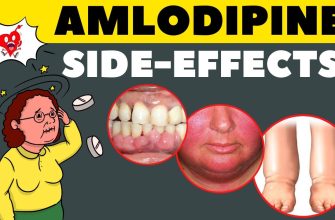
Before prescribing, assess the patient’s medical history for contraindications such as a history of tendon disorders, renal impairment, or any known allergies to fluoroquinolones. It’s advisable to inform the patient about potential side effects, including gastrointestinal discomfort and the risk of tendon rupture, particularly in older adults.
When writing the prescription, include the drug name, dosage, and duration of treatment. An example dosage for adults might be 500 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days, depending on the type of infection. Encourage the patient to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Lastly, provide clear instructions regarding the importance of staying hydrated and avoiding specific interactions, such as antacids containing magnesium or aluminum, as they can affect absorption. Regular follow-up appointments can be arranged to monitor the patient’s response to the treatment.
- Write Prescription for Levaquin
- Understanding Levaquin: An Overview
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects and Precautions
- Indications for Levaquin Use in Patients
- Common Indications
- Special Considerations
- Dosage Guidelines for Levaquin Prescribing
- General Dosage Recommendations
- Special Populations
- Assessing Patient Medical History for Levaquin
- Evaluate Existing Conditions
- Medication Interactions
- Possible Side Effects and Warnings for Levaquin
- Serious Side Effects
- Warnings
- Patient Counseling: What to Discuss Before Prescribing
- Common Drug Interactions with Levaquin
- Antacids and Sucralfate
- Warfarin
Write Prescription for Levaquin
To prescribe Levaquin, ensure the patient meets specific criteria based on their medical history and the infection being treated. Levaquin, or levofloxacin, is commonly used for bacterial infections, including respiratory and urinary tract infections. Start by verifying the patient’s allergies and contraindications, particularly regarding fluoroquinolones.
Follow these guidelines when writing the prescription:
| Dosage | Indication | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 250-750 mg once daily | Acute bacterial sinusitis | 5-10 days |
| 500 mg once daily | Pneumonia | 7-14 days |
| 250 mg once daily | Urinary tract infections | 3-10 days |
Adjust the dosage for patients with renal impairment. Recommend adequate hydration to prevent crystalluria. Inform patients about possible side effects, which include gastrointestinal disturbances, dizziness, or tendon rupture. Advise them to report any unusual symptoms immediately.
Always provide clear instructions on how to take Levaquin. Encourage adherence to the complete course, even if symptoms improve early. Consider potential interactions with other medications, such as antacids or supplements containing magnesium or aluminum, which can reduce absorption.
Confirm follow-up appointments to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and adjust as necessary. This proactive approach ensures optimal recovery for patients receiving Levaquin.
Understanding Levaquin: An Overview
Levaquin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic belonging to the fluoroquinolone class, primarily used to treat bacterial infections. It’s effective against a variety of pathogens, making it suitable for conditions such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. When prescribing Levaquin, ensure that the bacteria causing the infection are susceptible to this medication, as this enhances treatment success.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage of Levaquin varies based on the infection being treated. For most infections, doses typically range from 250 mg to 750 mg once daily. The duration of therapy usually lasts from 5 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection. It’s crucial to advise patients to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headache, and dizziness. Rare but serious adverse reactions can occur, such as tendon rupture and peripheral neuropathy. Patients with a history of tendon issues should use Levaquin cautiously. Regular assessment of renal function is necessary, as dosage adjustments may be required for individuals with kidney impairment. Encourage patients to stay well-hydrated during treatment.
Indications for Levaquin Use in Patients
Levaquin is primarily prescribed for treating infections caused by specific types of bacteria. Consider the following indications for its use:
Common Indications
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Levaquin effectively treats pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Urinary Tract Infections: It is indicated for complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Levaquin helps in addressing infections of the skin and associated structures.
- Bone and Joint Infections: Used for osteomyelitis and septic arthritis, ensuring targeted therapy for these conditions.
Special Considerations
- Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Levaquin may be beneficial in managing exacerbations.
- Immunocompromised Patients: Infections in individuals with weakened immune systems often respond to Levaquin.
- Travelers’ Diarrhea: This medication can be used for treating diarrhea caused by susceptible bacteria.
Before prescribing Levaquin, evaluate the patient’s medical history and potential drug interactions. Adhere to local guidelines and culture results whenever possible to ensure appropriate use.
Dosage Guidelines for Levaquin Prescribing
When prescribing Levaquin (levofloxacin), consider the specific indication and patient characteristics to determine the appropriate dosage. For most adult infections, the following guidelines serve as a solid foundation.
General Dosage Recommendations
- For uncomplicated urinary tract infections: 250 mg once daily for 3 days.
- For pneumonia (CAP): 500 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days; severe cases may require 750 mg once daily.
- For sinusitis: 500 mg once daily for 10 to 14 days.
- For skin infections: Typically 500 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days.
Ensure to adjust the dosage in patients with renal impairment. Monitor renal function and modify the dosage accordingly. For moderate impairment (CrCl 30-49 mL/min), reduce the dose by half.
Special Populations
- In elderly patients, consider starting with a lower dose, particularly if renal function is compromised.
- In pediatric patients, Levaquin is not approved for those under the age of 18 unless the potential benefits outweigh risks.
- For pregnant or breastfeeding women, assess the risk versus benefit as Levaquin passes into breast milk and may affect fetal development.
Always provide patients with clear instructions regarding the duration of therapy and the importance of adherence to the prescribed regimen to ensure optimal outcomes.
Assessing Patient Medical History for Levaquin
Review the patient’s medical history thoroughly before prescribing Levaquin. Focus on identifying any previous allergic reactions, particularly to fluoroquinolones, which may contraindicate its use.
Evaluate Existing Conditions
Assess for a history of tendon disorders, especially tendon ruptures, as Levaquin can increase the risk. Take note of any renal impairment; dosage adjustments may be necessary in such cases. Examine the patient’s history for neurologic disorders like epilepsy, as Levaquin can provoke seizures in predisposed individuals.
Medication Interactions
Check for current medications that may interact with Levaquin. Antacids, sucralfate, and some supplements can interfere with absorption. Review the list of current prescriptions, including anticoagulants, as Levaquin may enhance their effects. This careful evaluation helps prevent adverse effects and maximizes the benefits of treatment.
Possible Side Effects and Warnings for Levaquin
Levaquin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, can cause various side effects that users should be aware of. Common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, insomnia, and headaches. If you experience any of these, consult your healthcare provider for advice.
Serious Side Effects
Some side effects can be more severe and require immediate medical attention:
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Tendinitis or Tendon Rupture | Risk increases especially for older adults or those on corticosteroids. |
| Neuropathy | May cause pain, burning, or tingling sensations. |
| QT Prolongation | Can lead to serious heart rhythms; monitor for fainting or irregular heartbeat. |
| Severe Allergic Reactions | Symptoms include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. |
Warnings
Consider these warnings before using Levaquin:
- Not suitable for individuals with a history of tendon disorders or Myasthenia gravis.
- Use caution if you have kidney disease; dosage adjustments may be necessary.
- Avoid using with certain medications, such as NSAIDs, which may increase the risk of CNS stimulation.
Always communicate any pre-existing conditions or medications you are taking to your healthcare provider to ensure safe use of Levaquin. Regular follow-ups can help monitor your reaction to treatment.
Patient Counseling: What to Discuss Before Prescribing
Discuss the patient’s allergies to antibiotics, specifically fluoroquinolones, before prescribing Levaquin. Confirm their medication history to identify potential drug interactions. Emphasize the risks of tendonitis and tendon rupture, especially in individuals over 60 or those on corticosteroids.
Clarify indications for Levaquin, such as bacterial infections, and stress the importance of adherence to prescribed dosing to prevent resistance. Offer guidance on potential side effects, including gastrointestinal upset, dizziness, and central nervous system effects. Encourage patients to report unusual symptoms immediately.
Address the importance of hydration during treatment to reduce the risk of kidney complications. Suggest avoiding excessive sunlight or tanning beds, as Levaquin can increase photosensitivity. Additionally, recommend that pregnant or breastfeeding patients consult with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Encourage open communication throughout the course of treatment. Ensure patients understand when to seek medical advice if symptoms do not improve, or worsen. Provide printed information about Levaquin, if available, to reinforce what you discuss during the counseling session.
Common Drug Interactions with Levaquin
Levaquin, or levofloxacin, can interact with various medications, leading to altered effects or increased side effects. It’s vital to monitor these interactions carefully.
Antacids and Sucralfate
Avoid taking antacids containing aluminum, magnesium, or calcium within two hours of taking Levaquin. These compounds can reduce Levaquin’s absorption, decreasing its effectiveness. If you’re using sucralfate, space it out by at least two hours as well to prevent interaction.
Warfarin
When using Levaquin with warfarin, closely monitor your INR levels. Levaquin can enhance the anticoagulant effects, raising the risk of bleeding. Regular assessments and possible dosage adjustments of warfarin may be necessary during and after Levaquin therapy.
Consult your healthcare provider for any concerns about potential drug interactions or if you are on multiple medications. Always disclose your complete medication list before starting Levaquin.